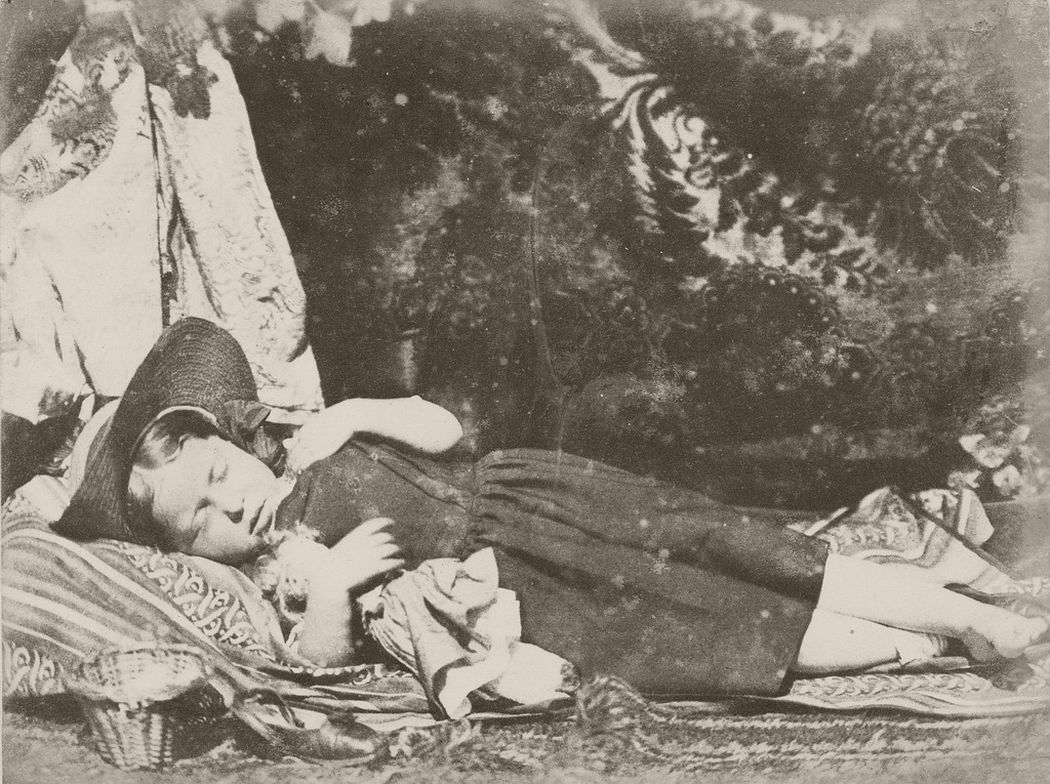
In 1843 painter David Octavius Hill joined engineer Robert Adamson to form Scotland’s first photographic studio. During their brief partnership that ended with Adamson’s untimely death, Hill & Adamson produced “the first substantial body of self-consciously artistic work using the newly invented medium of photography.”
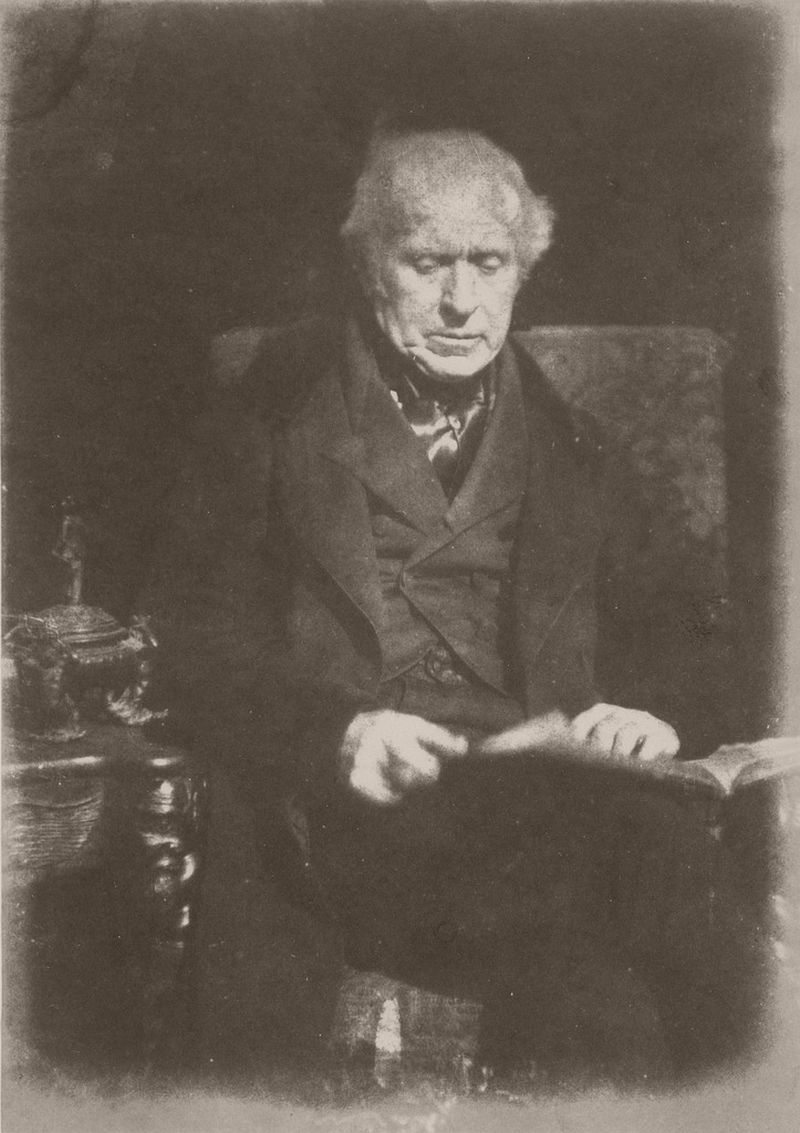
Their collaboration, with Hill providing skill in composition and lighting, and Adamson considerable sensitivity and dexterity in handling the camera, proved extremely successful, and they soon broadened their subject matter. Adamson’s studio, “Rock House”, on the Calton Hill in Edinburgh became the centre of their photographic experiments. Using the calotype process, they produced a wide range of portraits depicting well-known Scottish luminaries of the time, including Hugh Miller, both in the studio and in outdoors settings, often amongst the elaborate tombs in Greyfriars Kirkyard.
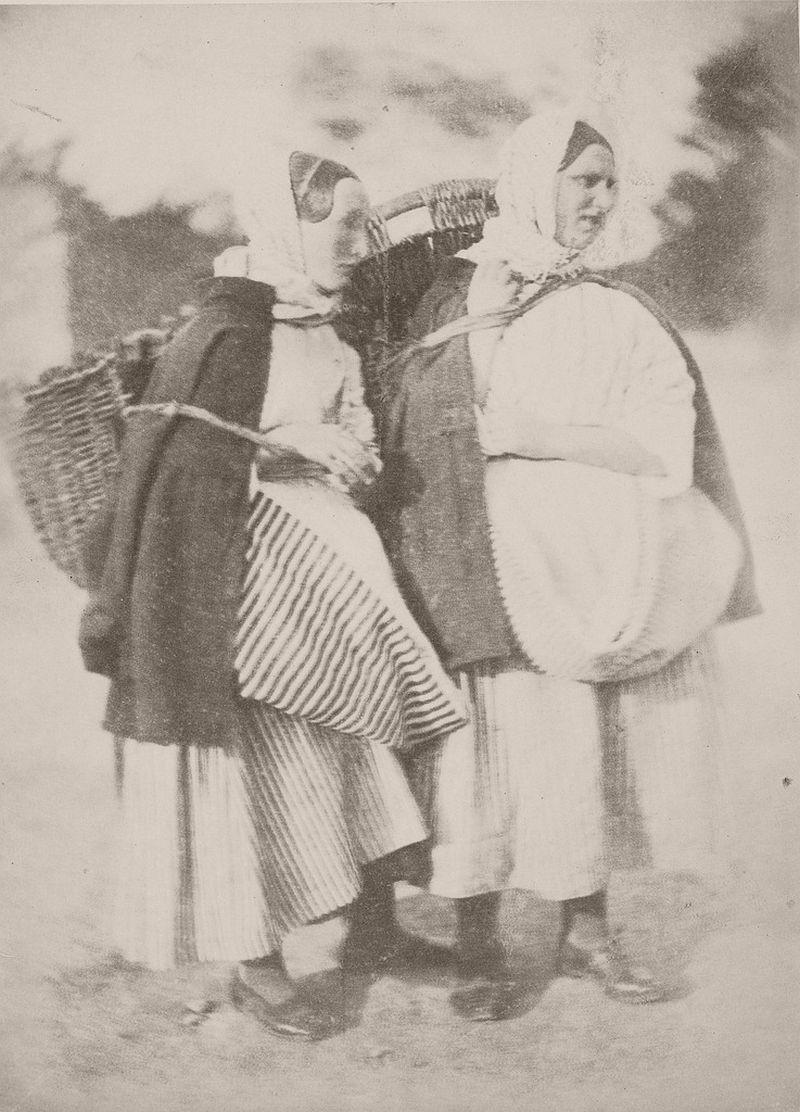
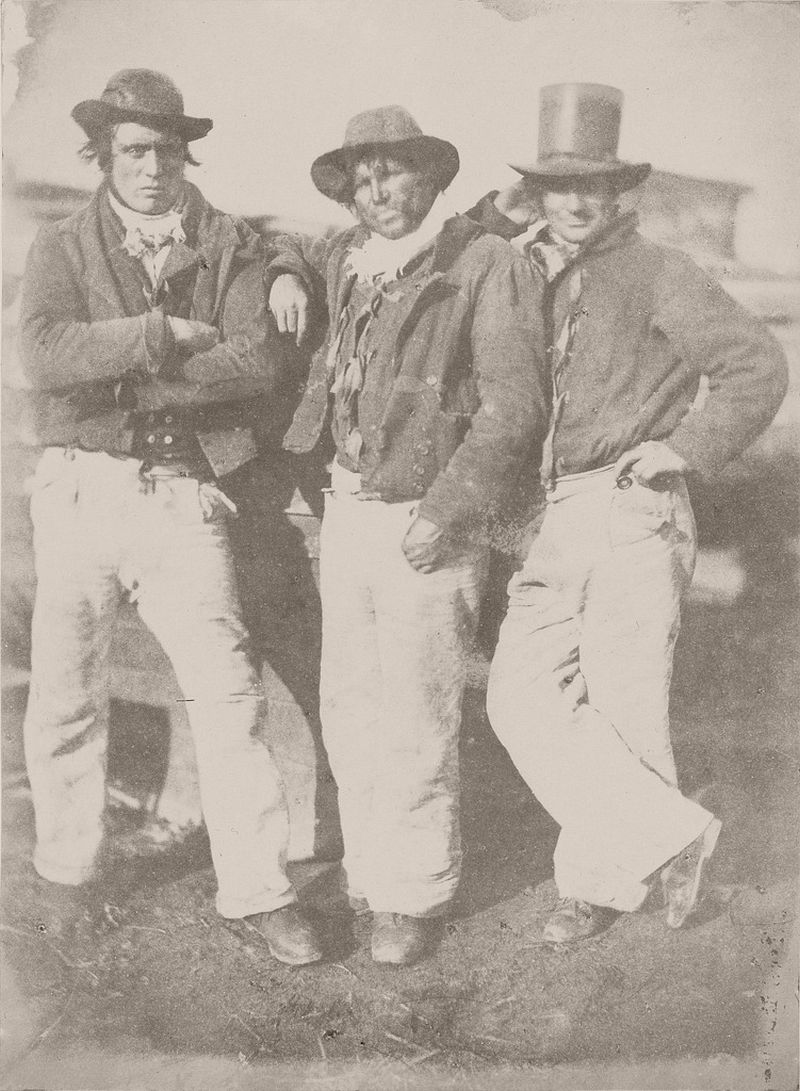
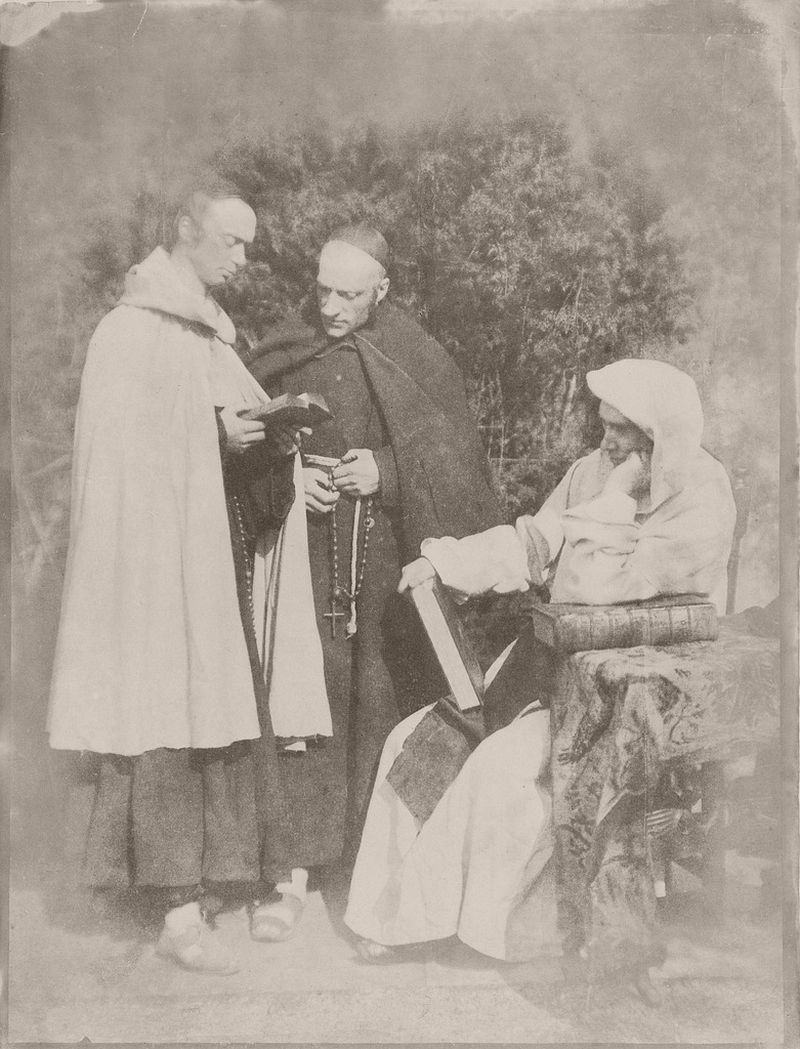
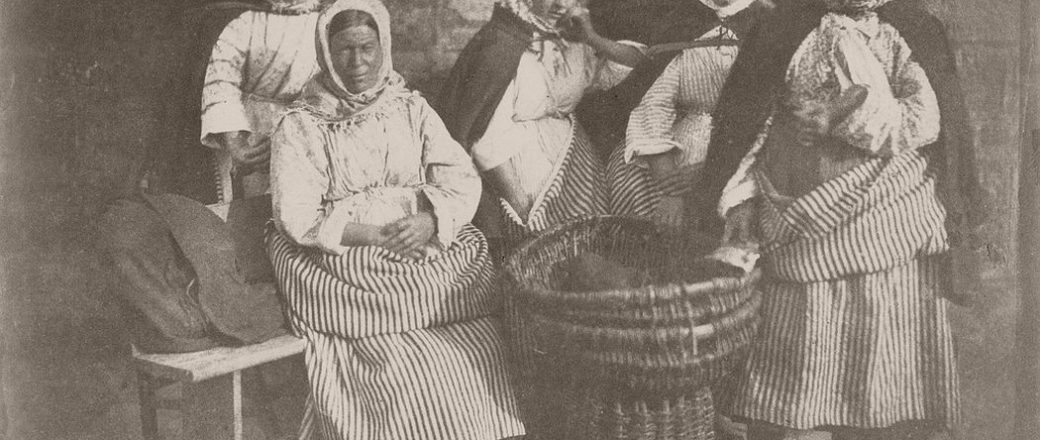
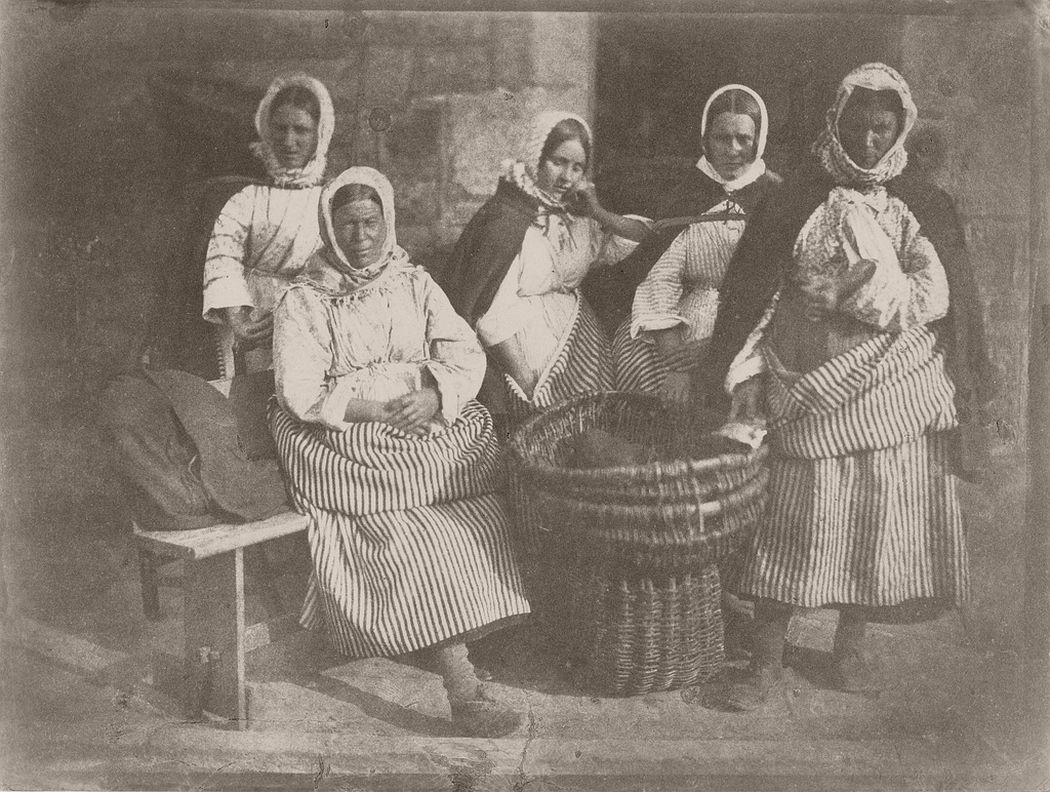
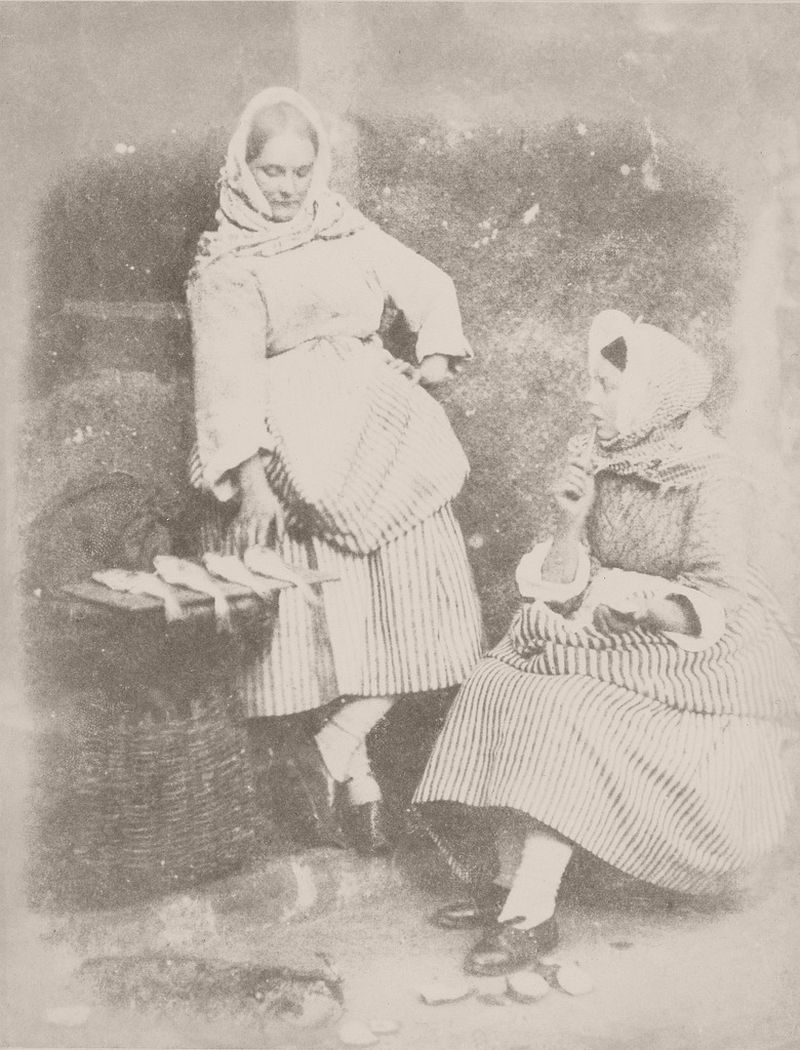
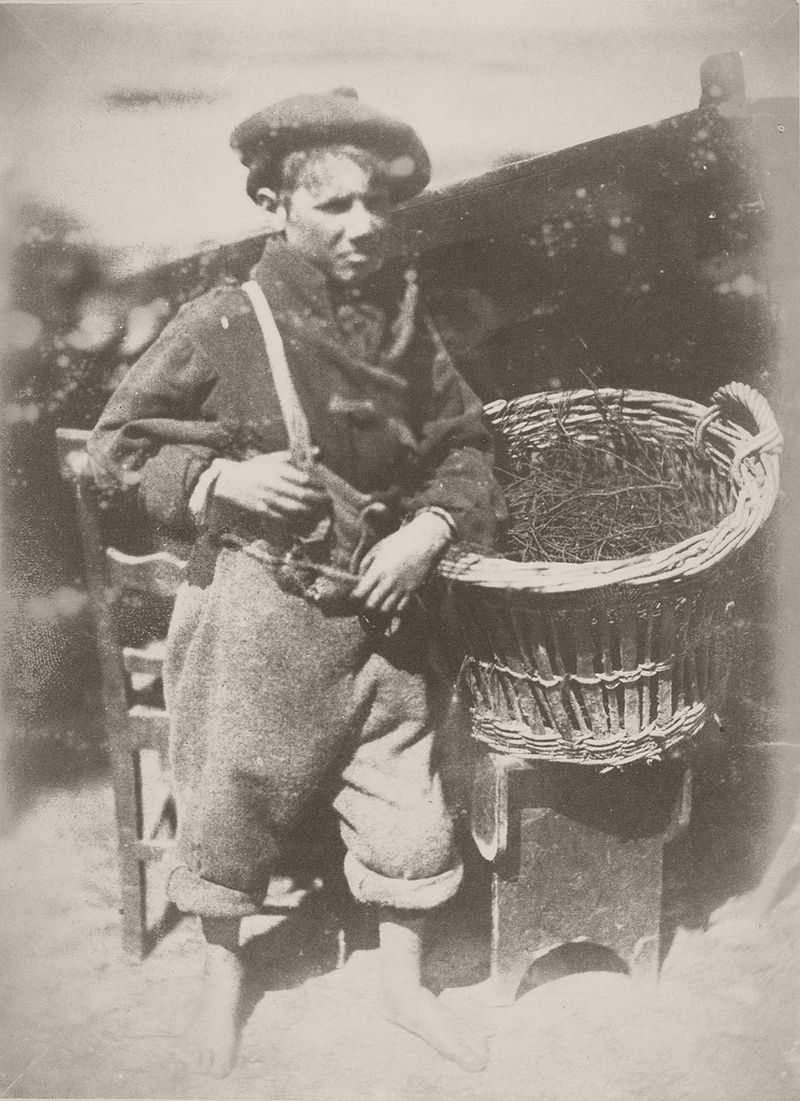
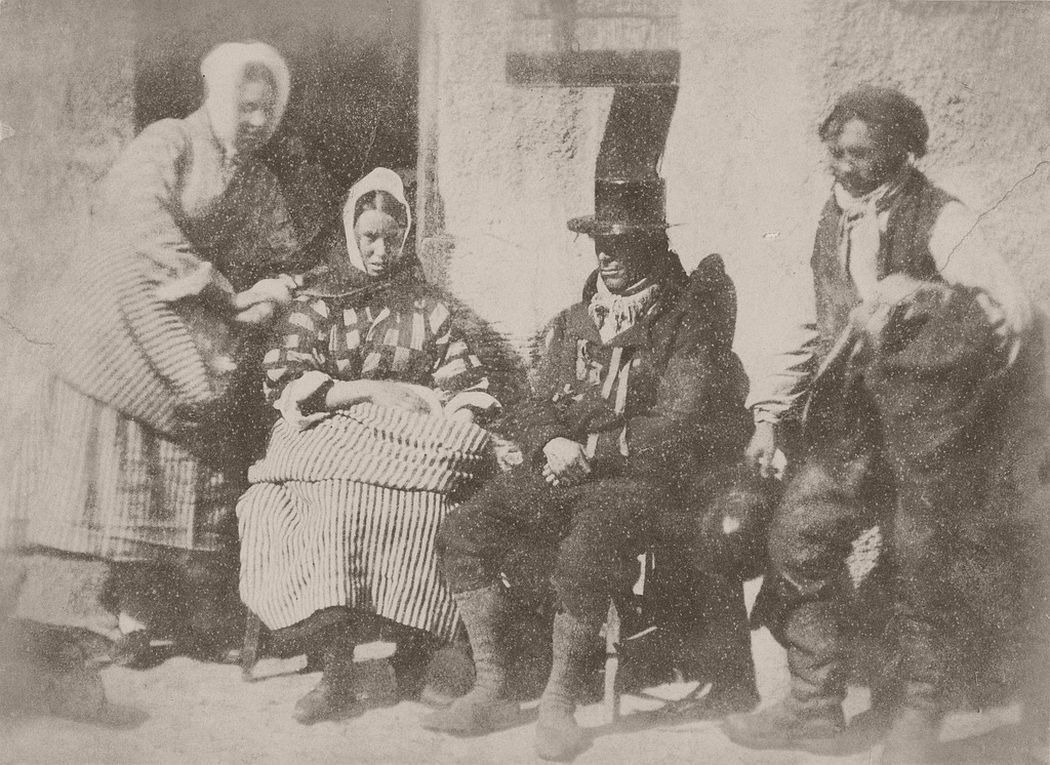
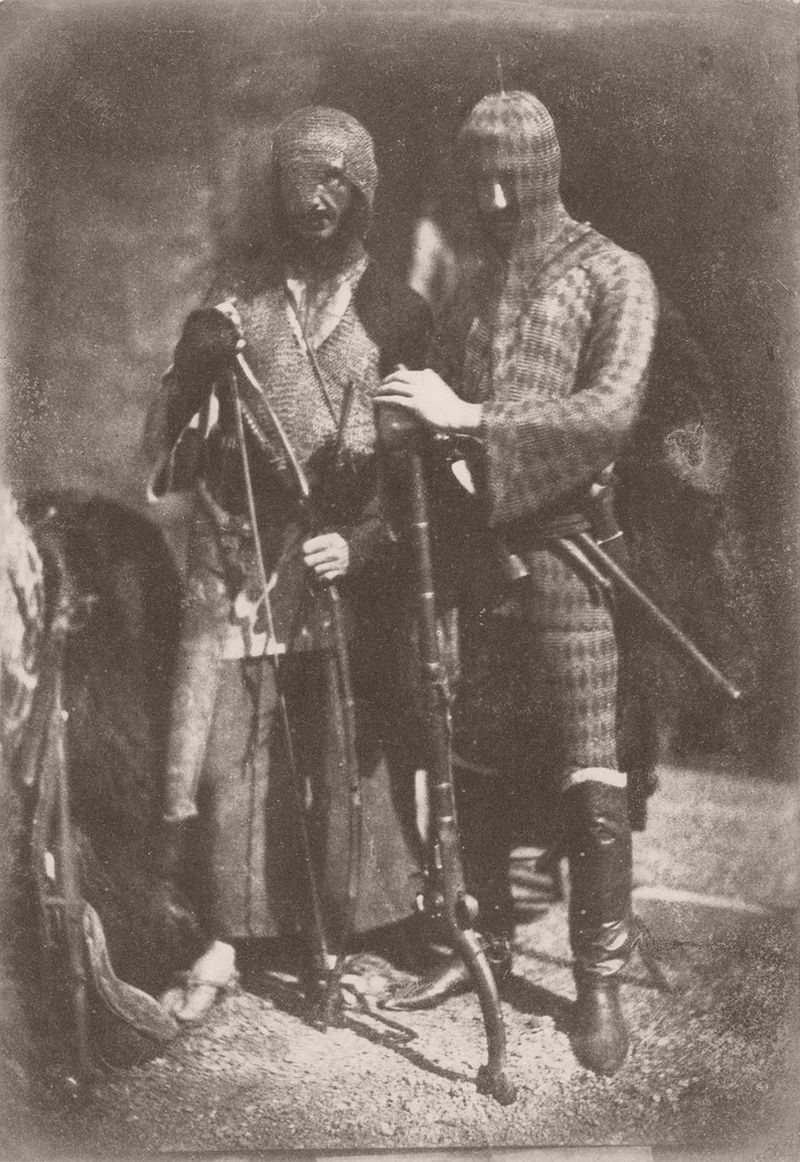
They photographed local and Fife landscapes and urban scenes, including images of the Scott Monument under construction in Edinburgh. As well as the great and the good, they photographed ordinary working folk, particularly the fishermen of Newhaven, and the fishwives who carried the fish in creels the 3 miles (5 km) uphill to the city of Edinburgh to sell them round the doors, with their cry of “Caller herrin” (fresh herring). They produced several groundbreaking “action” photographs of soldiers and – perhaps their most famous photograph – two priests walking side by side.
Their partnership produced around 3,000 different photographs, but was cut short after only four years due to the ill health and untimely death of Adamson in 1848. Hill became less active and abandoned the studio after several months, but continued to sell prints of the photographs and use them as an aid for composing paintings.

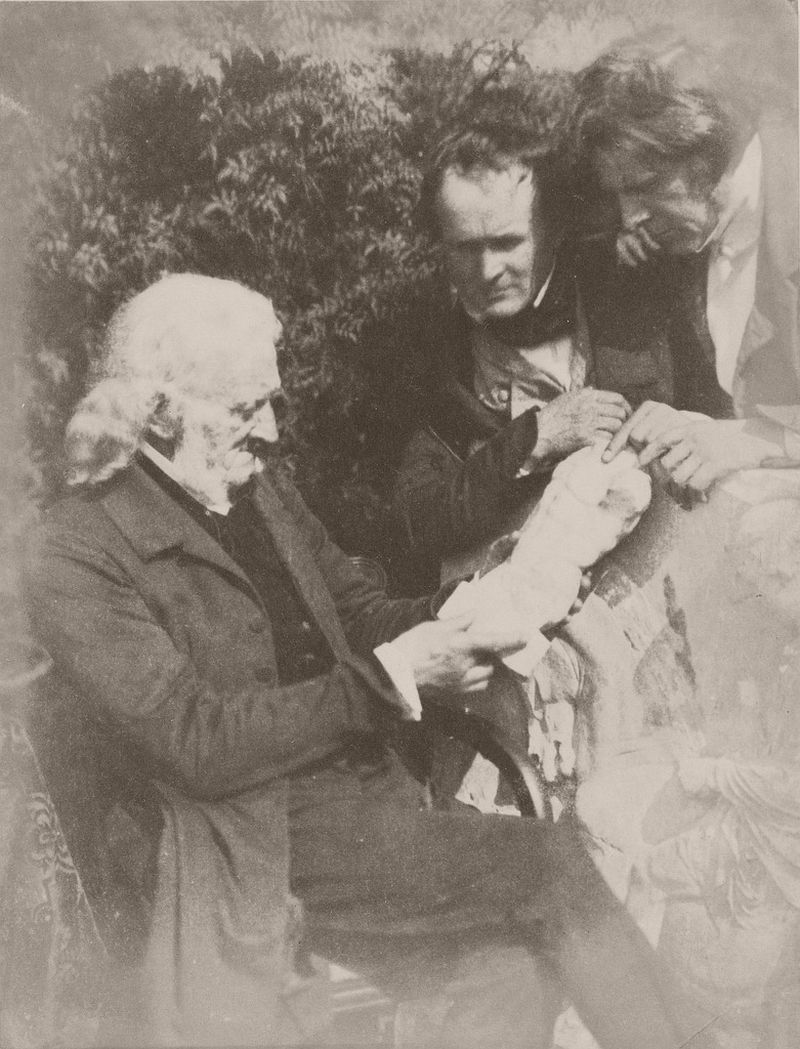
Greyfriars’ Churchyard, the Dennistoun Monument with D. O. Hill and His Nieces, 1843 – 1847, Photo: Hill & Adamson
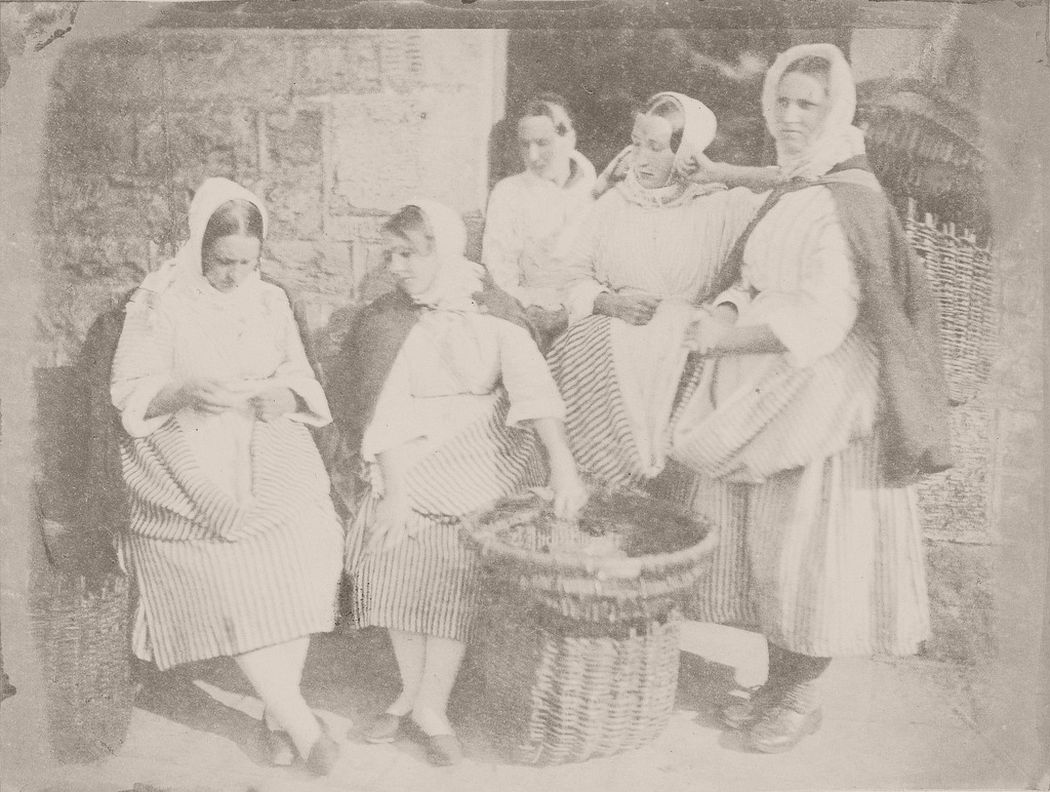

Two unknown women, Mrs Margaret (Dryburgh) Lyall, Marion Finlay and Mrs Grace (Finlay) Ramsay, 1843 – 1847, Photo: Hill & Adamson

Mrs. Elizabeth Cockburn Cleghorn and John Henning as Miss Wardour and Eddie Ochiltree from Sir Walter Scott’s “The Antiquary”, 1843 – 1847, Photo: Hill & Adamson

William Borthwick Johnstone, William Leighton Leith and David Scott, 1843 – 1847, Photo: Hill & Adamson
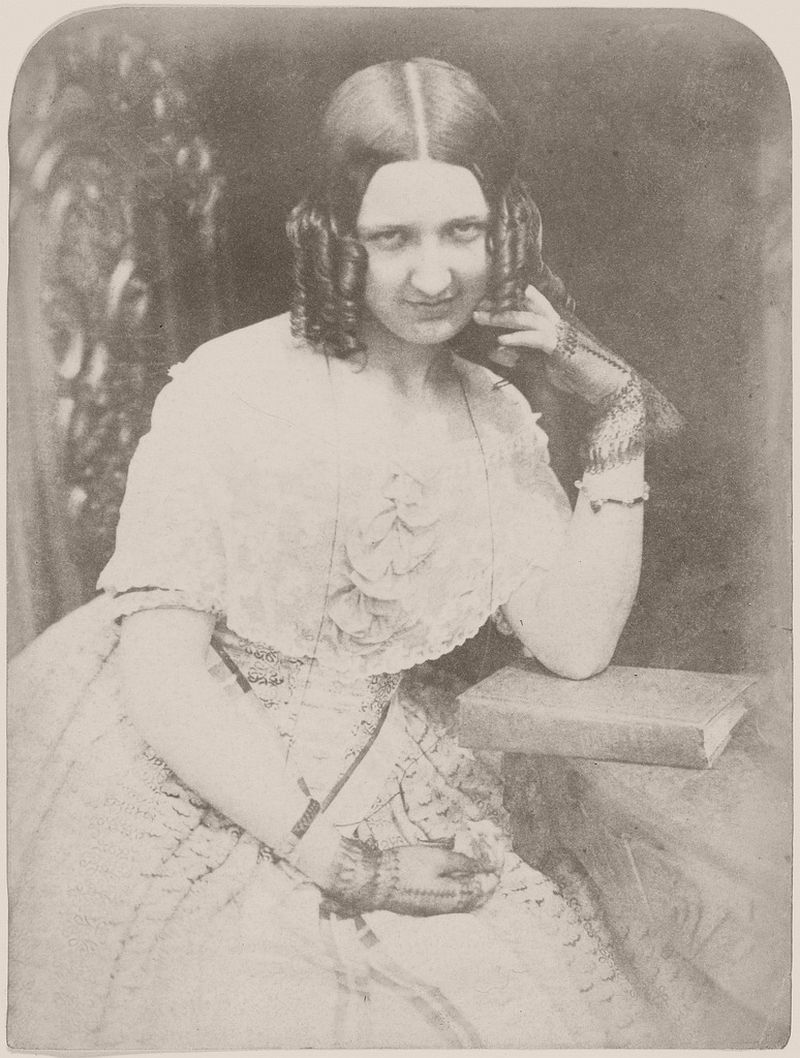



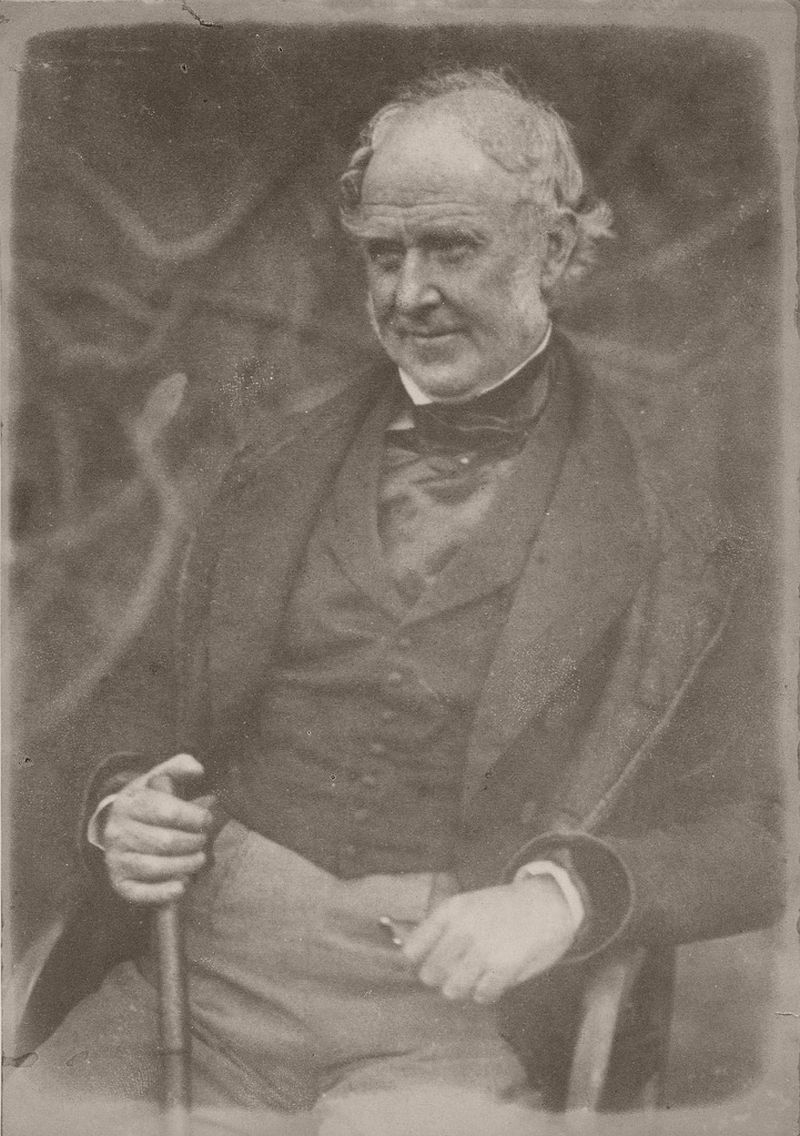










![Elizabeth Rigby [Lady Eastlake], 1843](https://monovisions.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/hill-adamson-xix-century-photographic-duo-11.jpg)






