In the 1830s, the District’s southern territory of Alexandria went into economic decline partly due to neglect by Congress. The city of Alexandria was a major market in the American slave trade, and pro-slavery residents feared that abolitionists in Congress would end slavery in the District, further depressing the economy. Alexandria’s citizens petitioned Virginia to take back the land it had donated to form the District, through a process known as retrocession.
The Virginia General Assembly voted in February 1846 to accept the return of Alexandria and on July 9, 1846, Congress agreed to return all the territory that had been ceded by Virginia. Therefore, the District’s current area consists only of the portion originally donated by Maryland. Confirming the fears of pro-slavery Alexandrians, the Compromise of 1850 outlawed the slave trade in the District, although not slavery itself.
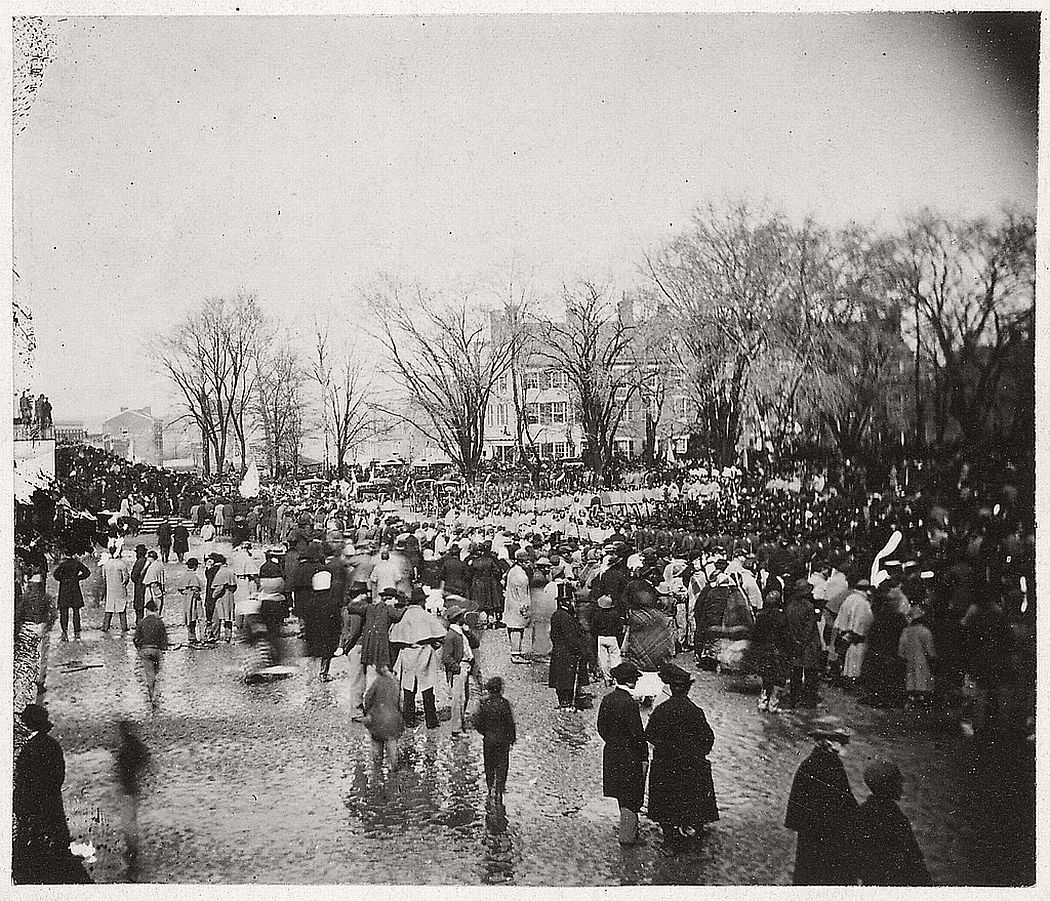
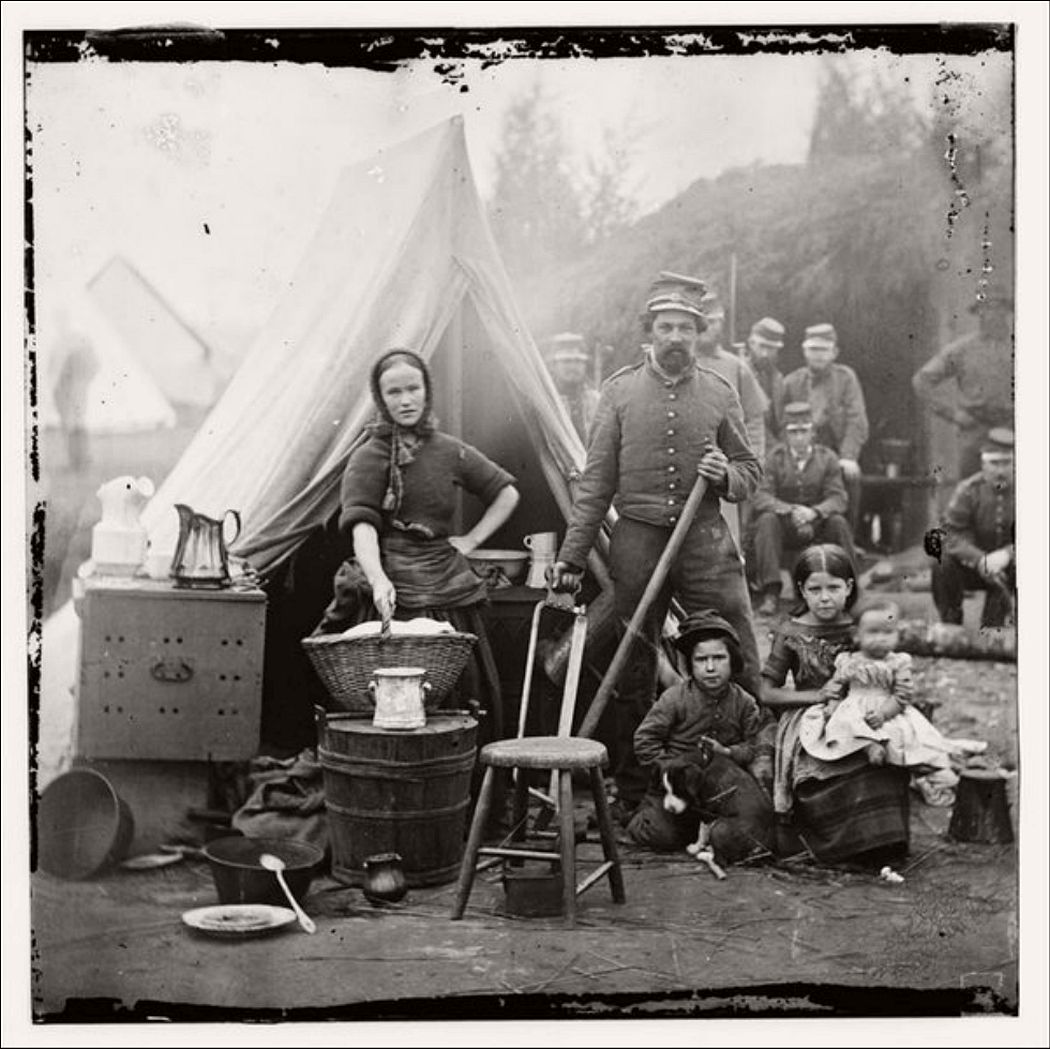
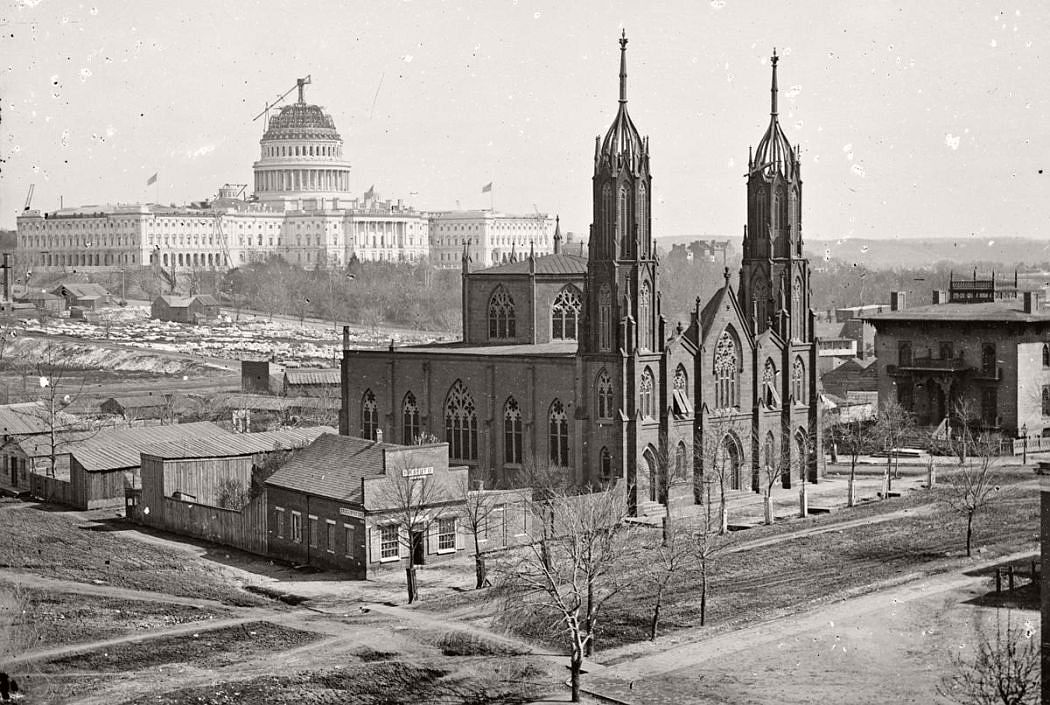
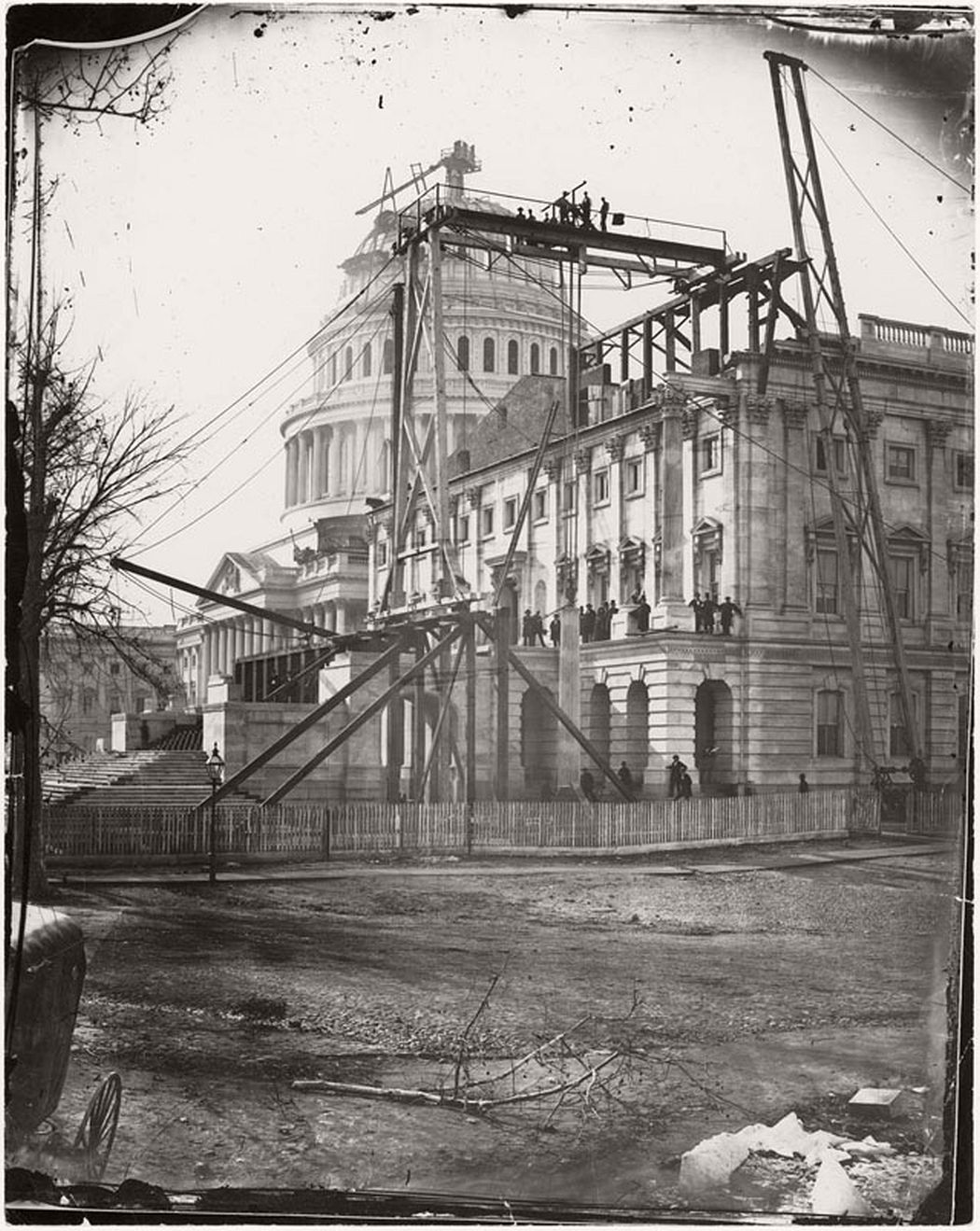
The outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861 led to expansion of the federal government and notable growth in the District’s population, including a large influx of freed slaves. President Abraham Lincoln signed the Compensated Emancipation Act in 1862, which ended slavery in the District of Columbia and freed about 3,100 enslaved persons, nine months prior to the Emancipation Proclamation. In 1868, Congress granted the District’s African American male residents the right to vote in municipal elections.