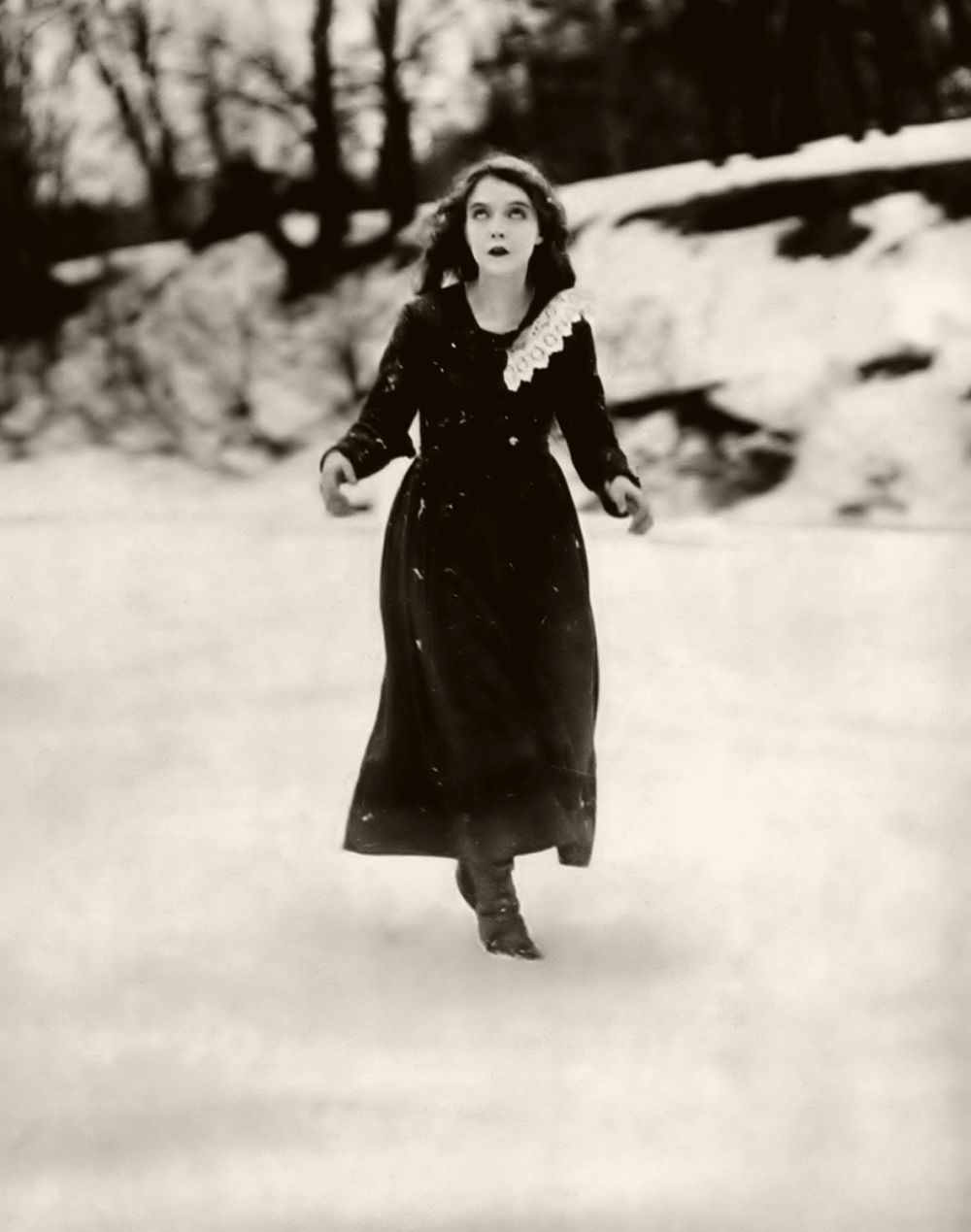
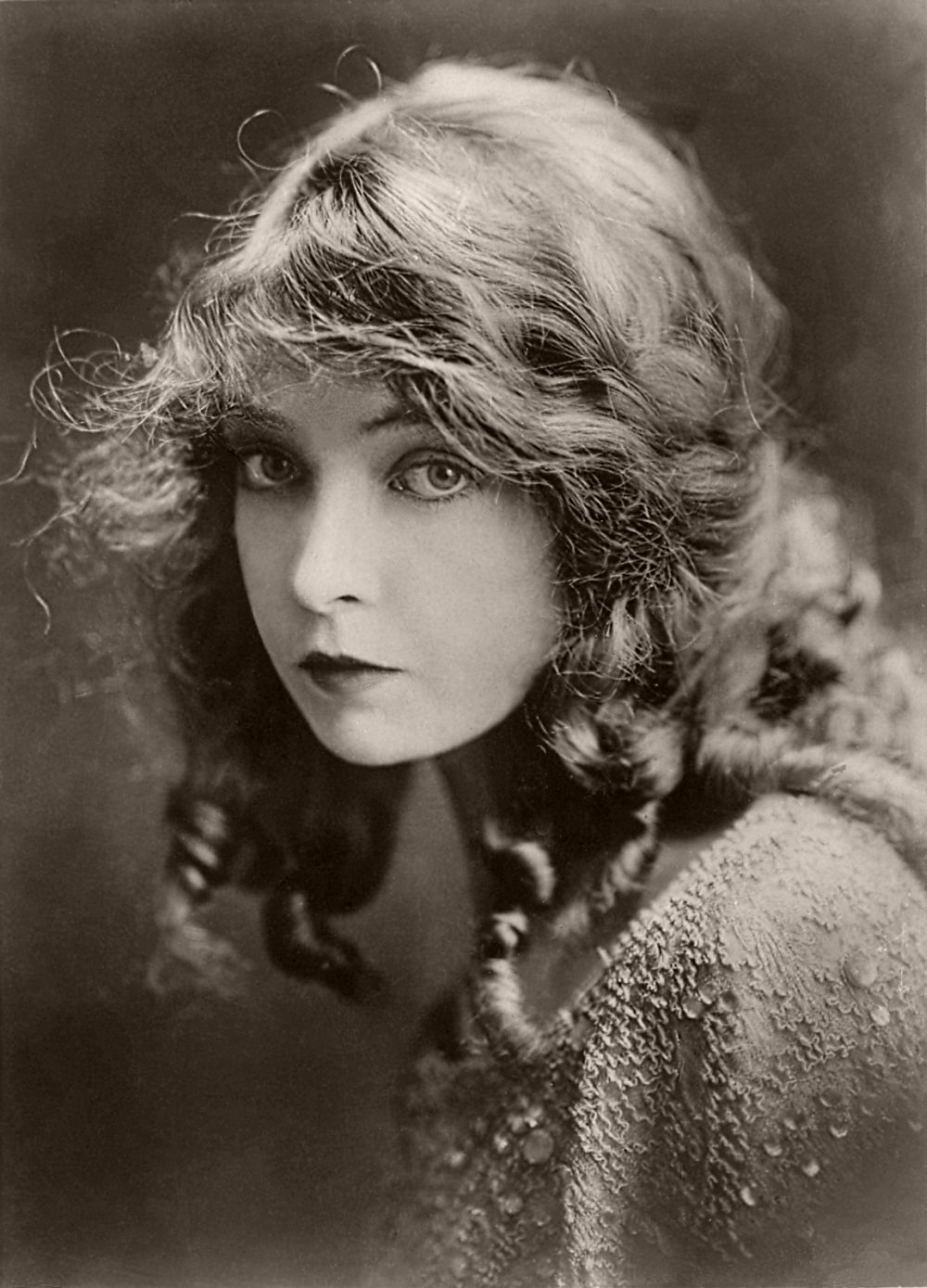
After 10 years of acting on the stage, she made her film debut opposite Dorothy in Griffith’s short film An Unseen Enemy (1912). At the time established thespians considered “the flickers” a rather base form of entertainment, but she was assured of its merits. Gish continued to perform on the stage, and in 1913, during a run of A Good Little Devil, she collapsed from anemia. Lillian would take suffering for her art to the extreme in a film career which became her obsession. One of the enduring images of Gish’s silent film years is the climax of the melodramatic Way Down East, in which Gish’s character floats unconscious on an ice floe towards a raging waterfall, her long hair and hand trailing in the water. Her performance in these frigid conditions gave her lasting nerve damage in several fingers. Similarly, when preparing for her death scene in La Bohème over a decade later, Gish reportedly did not eat and drink for three days beforehand, causing the director to fear he would be filming the death of his star as well as of the character.
Lillian starred in many of Griffith’s most acclaimed films, including The Birth of a Nation (1915), Intolerance (1916), Broken Blossoms (1919), Way Down East (1920), and Orphans of the Storm (1921). Griffith utilized Lillian’s expressive talents to the fullest, developing her into a suffering yet strong heroine. Having appeared in over 25 short films and features in her first two years as a movie actress, Lillian became a major star, becoming known as “The First Lady of American Cinema” and appearing in lavish productions, frequently of literary works such as Way Down East. She became the most esteemed actress of budding Hollywood cinema.
She directed her sister Dorothy in one film, Remodeling Her Husband (1920), when D. W. Griffith took his unit on location. He told Gish that he thought the crew would work harder for a girl. Gish never directed again, telling reporters at the time that directing was a man’s job. Unfortunately the film is now thought to be lost.
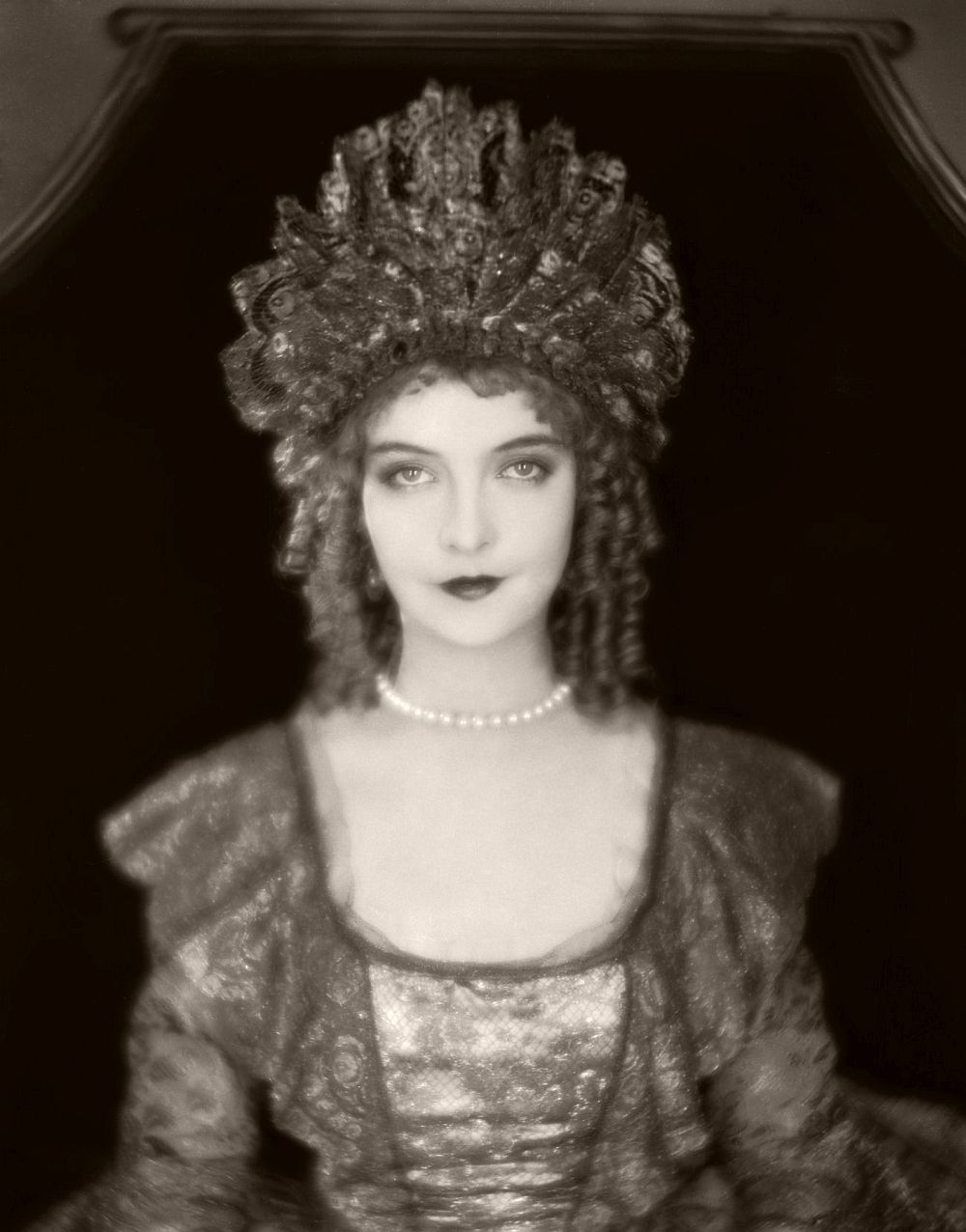

29th September 1926: Lillian Gish (1893 – 1993) plays the real-life Scottish heroine of the film ‘Annie Laurie’, directed by John S Robertson.
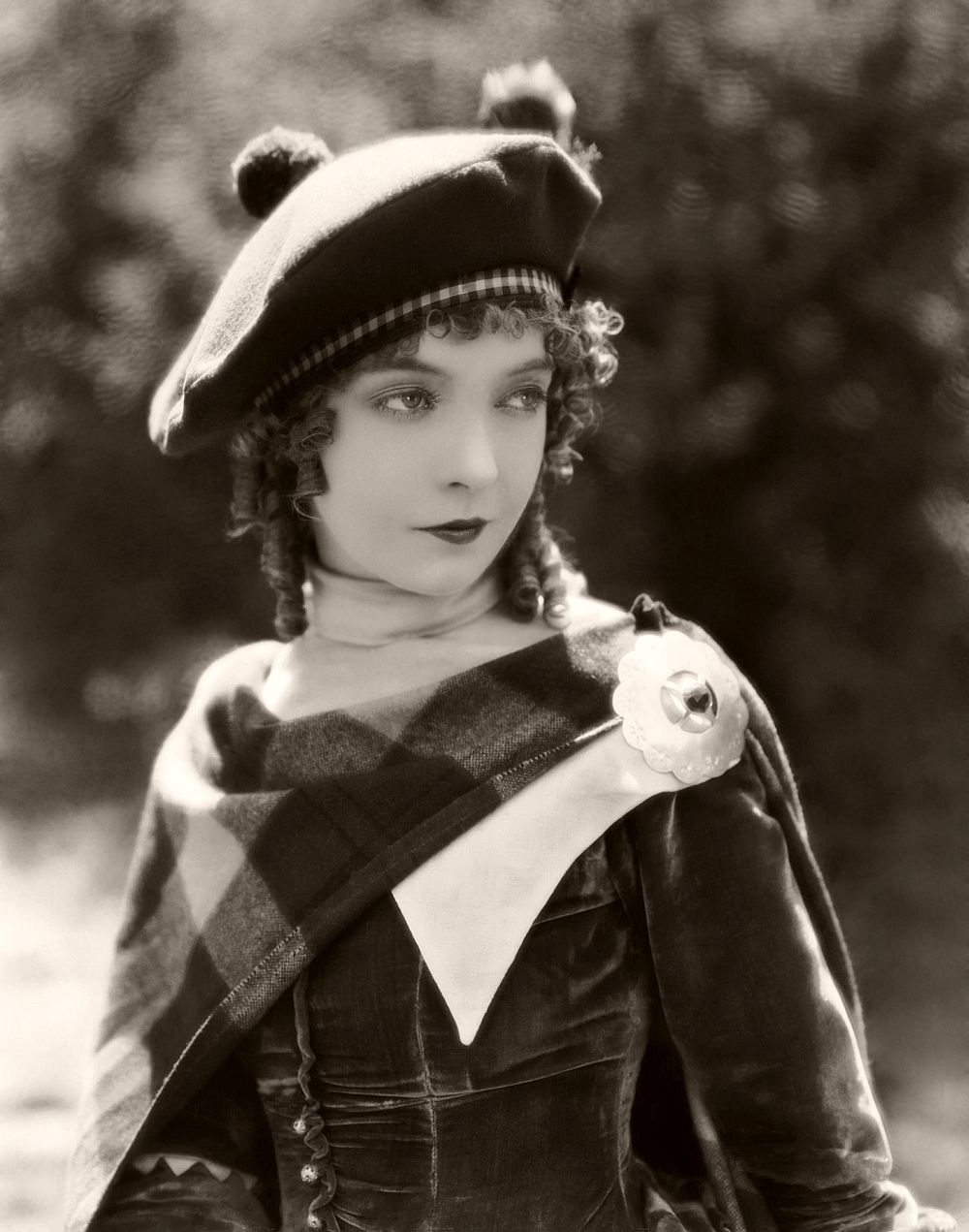

12th August 1926: Lillian Gish (1893 – 1993) plays the real-life Scottish heroine of the film ‘Annie Laurie’, directed by John S Robertson.
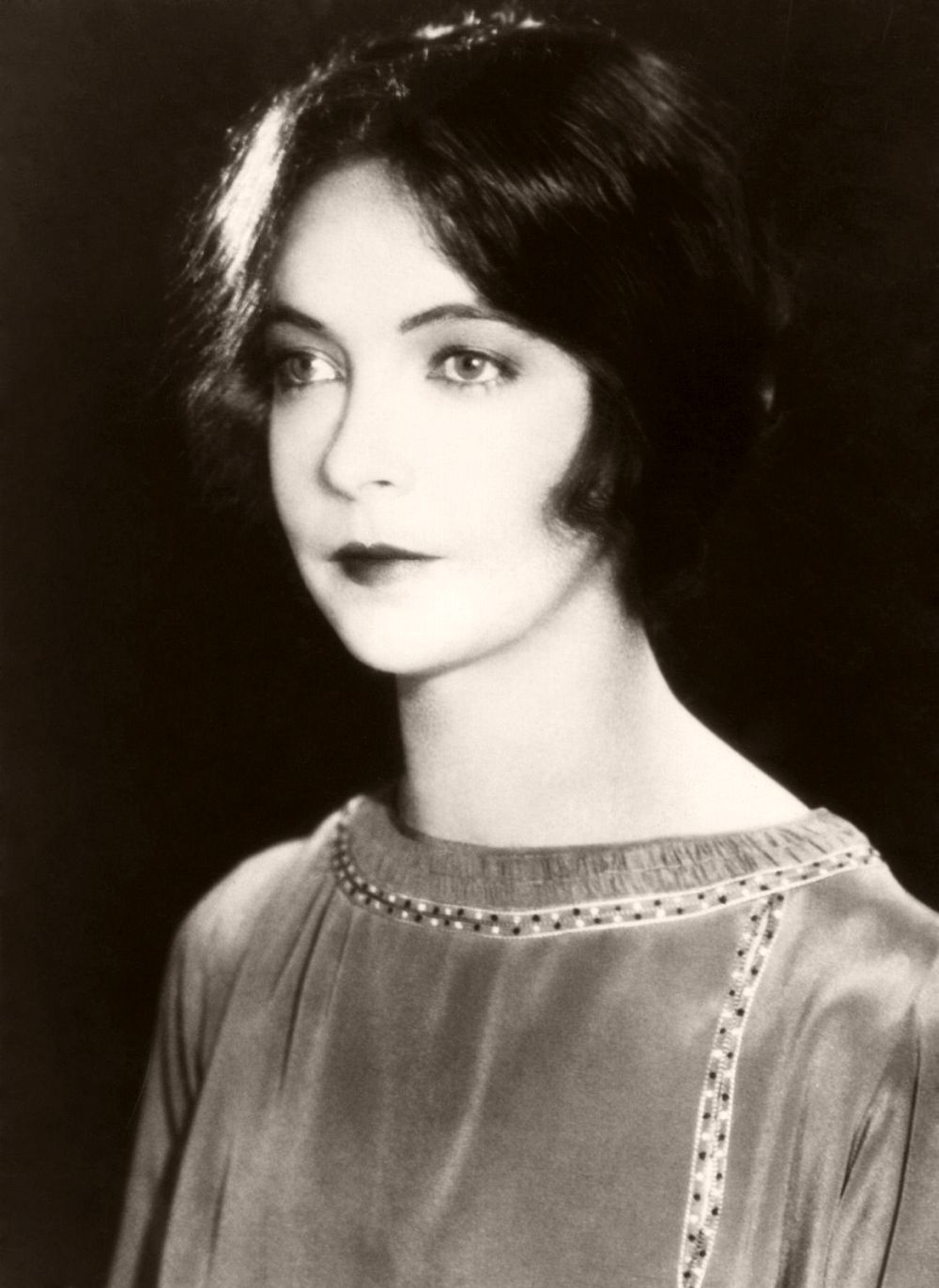

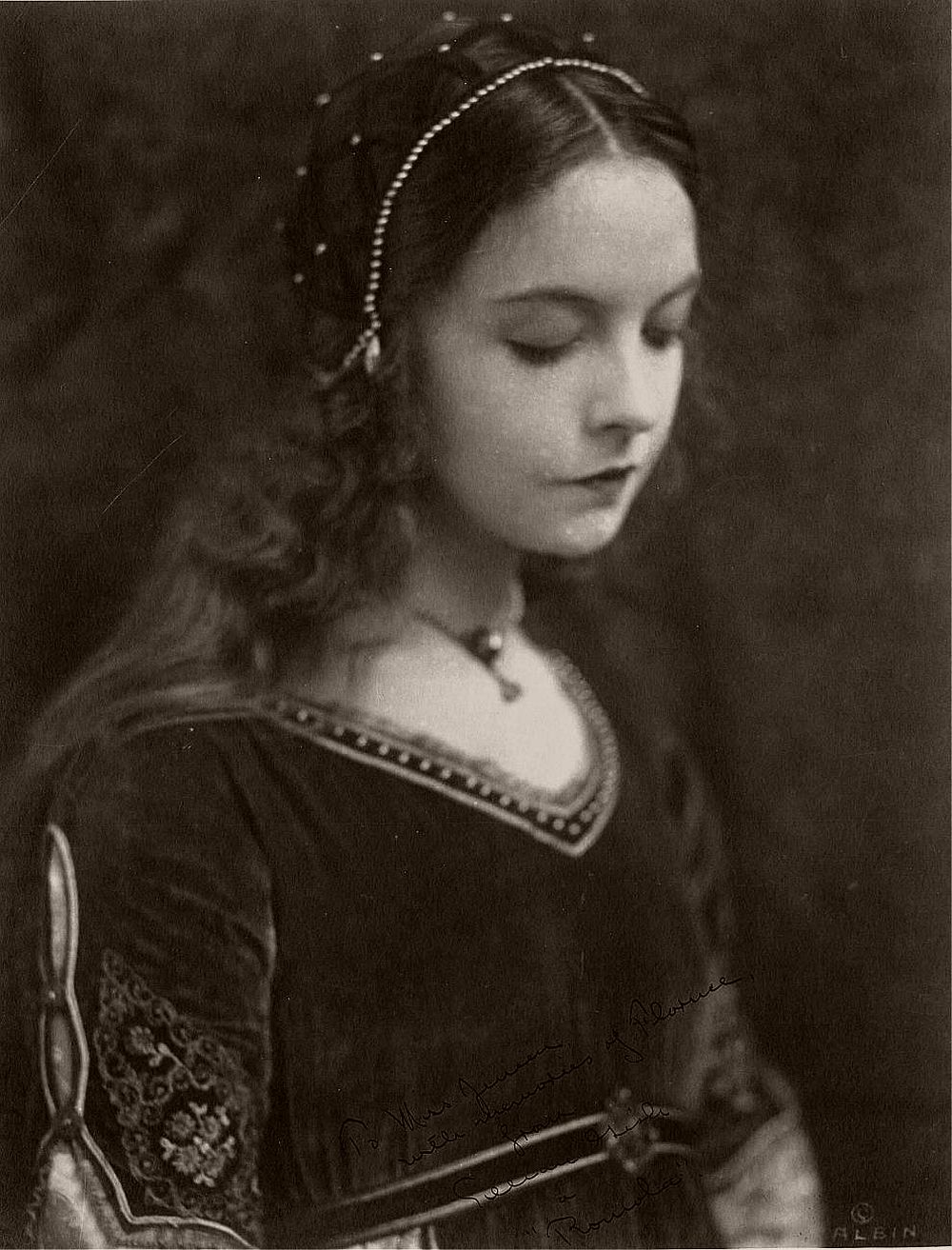
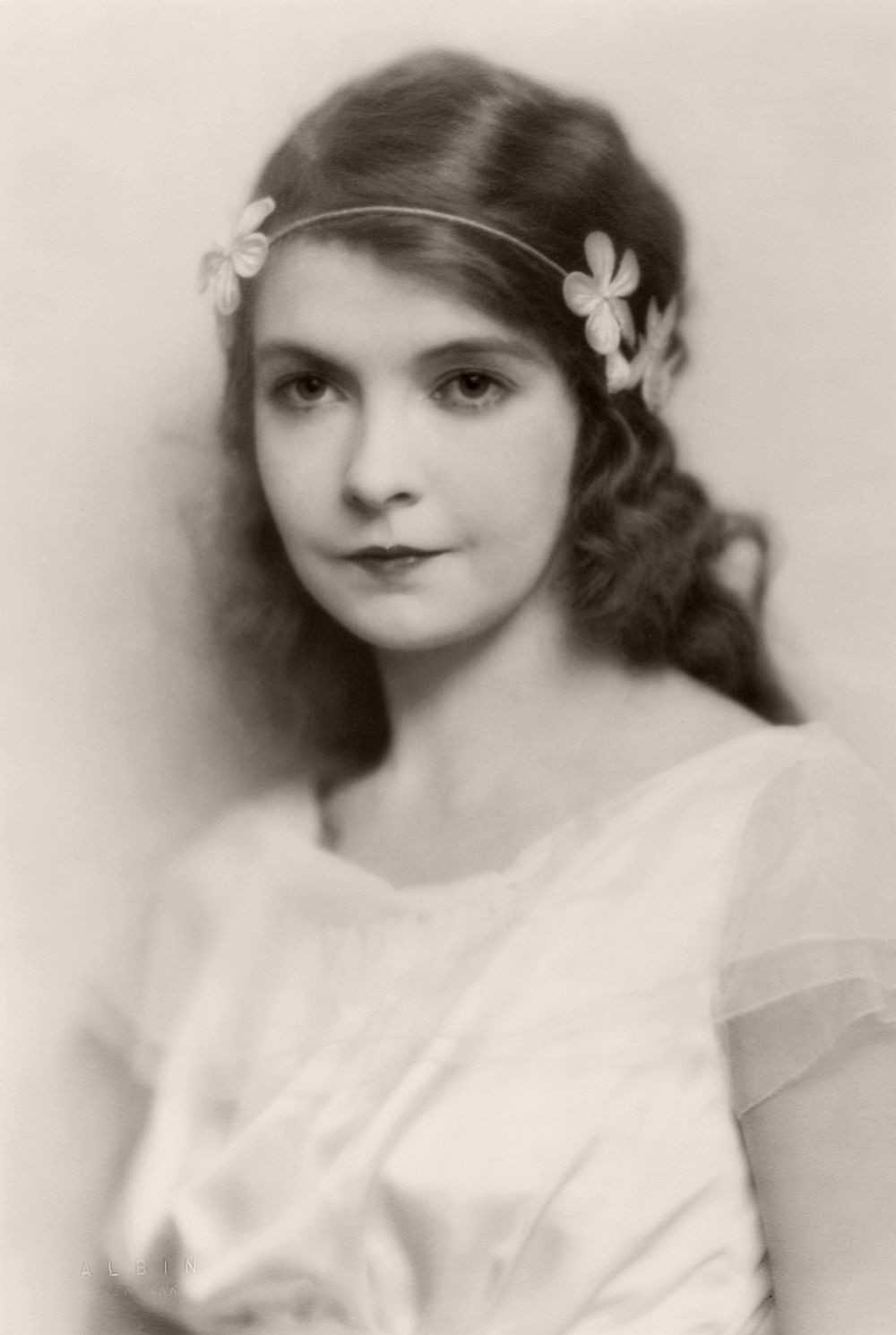
1923: Lillian Diana Gish, originally Lillian de Guiche (1893 – 1993), made her stage debut at the age of 5. She played a lot of waif type heroines during her silent film career but never quite made the successful transition to talking pictures. An Academy Award was presented to her in 1971.
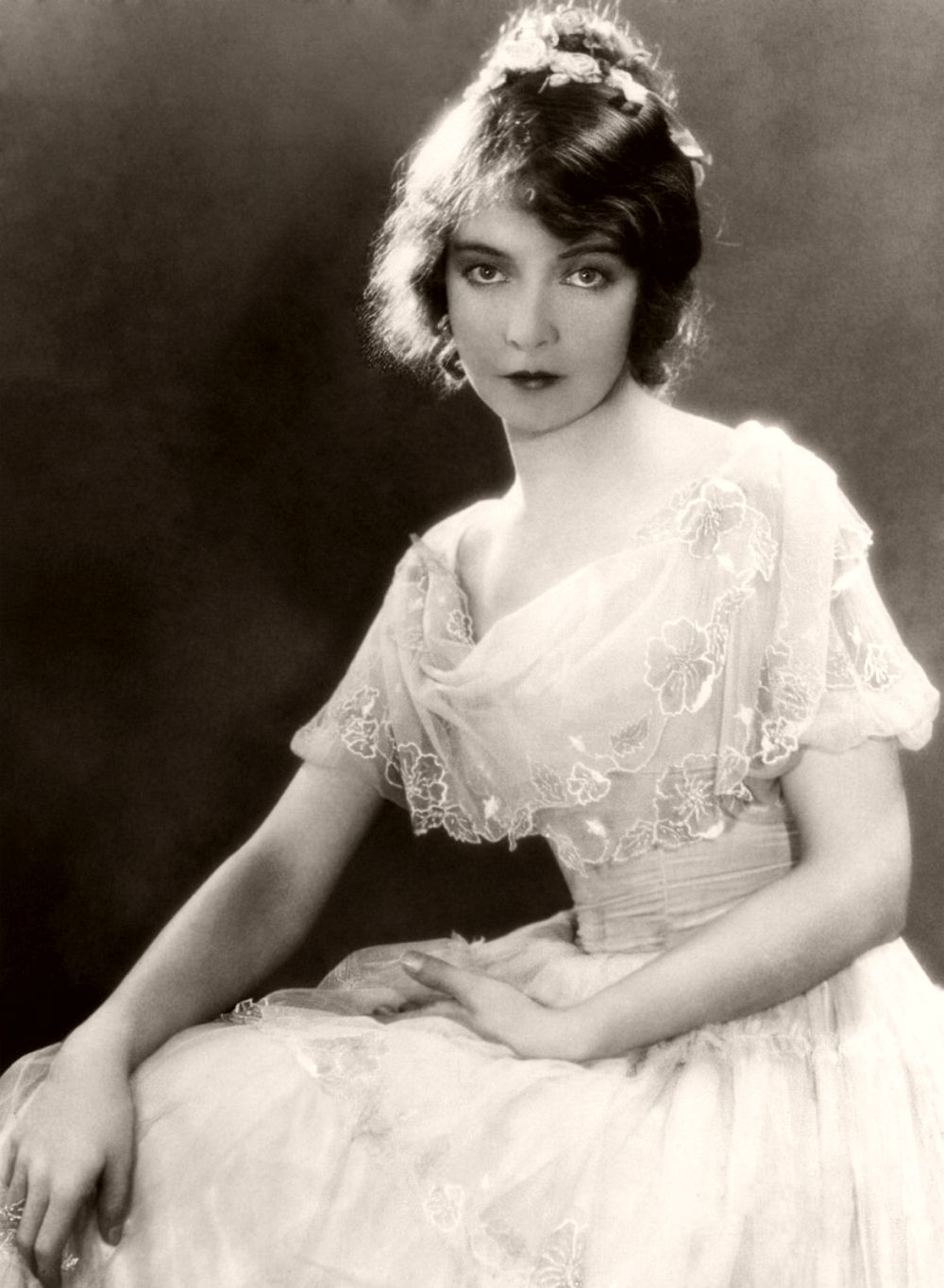

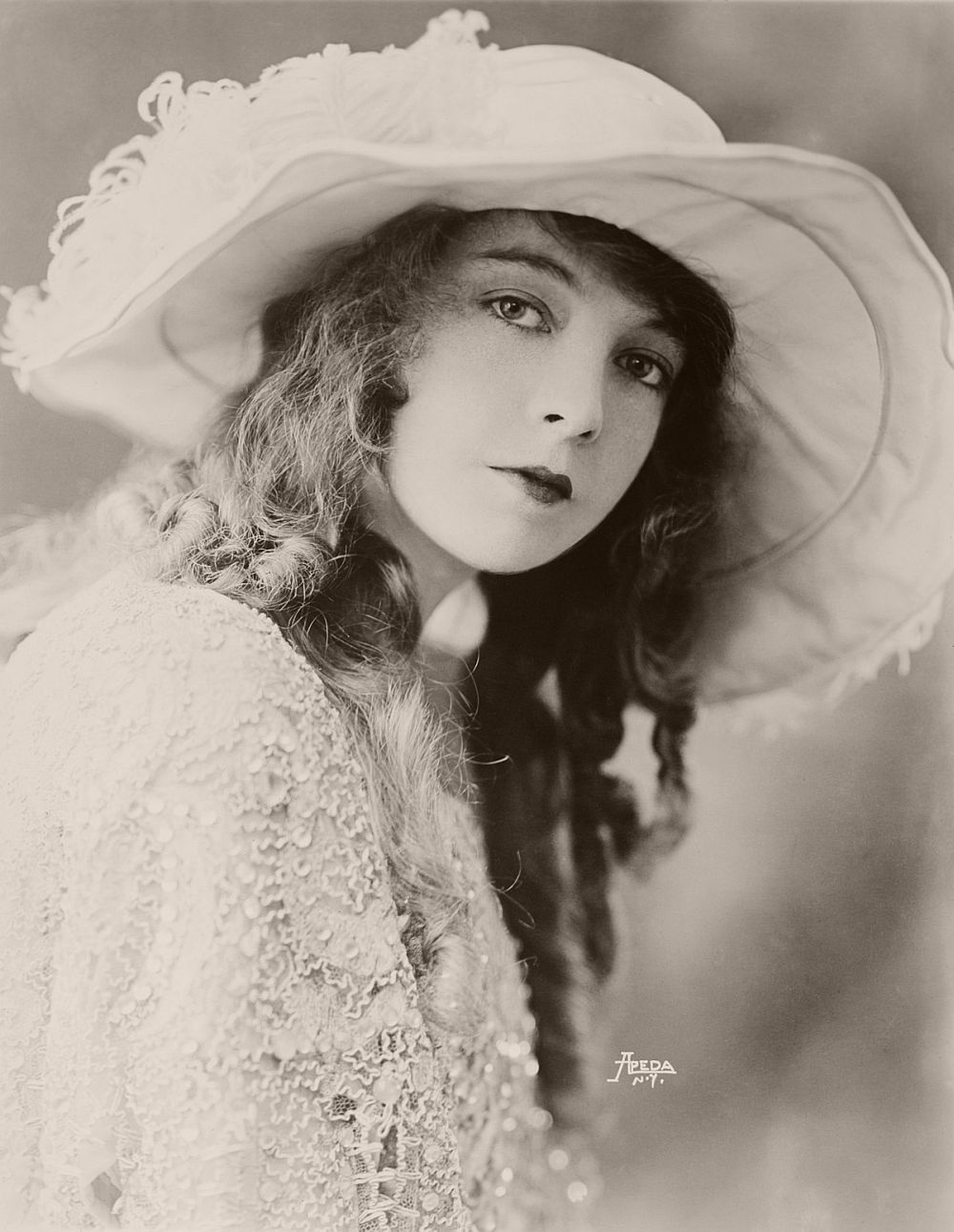
circa 1922: Lillian Diana Gish, originally Lillian de Guiche (1893 – 1993), made her stage debut at the age of 5. She played a lot of waif type heroines during her silent film career but never quite made the successful transition to talking pictures. She returned to the stage in 1930. An Academy Award was presented to her in 1971.
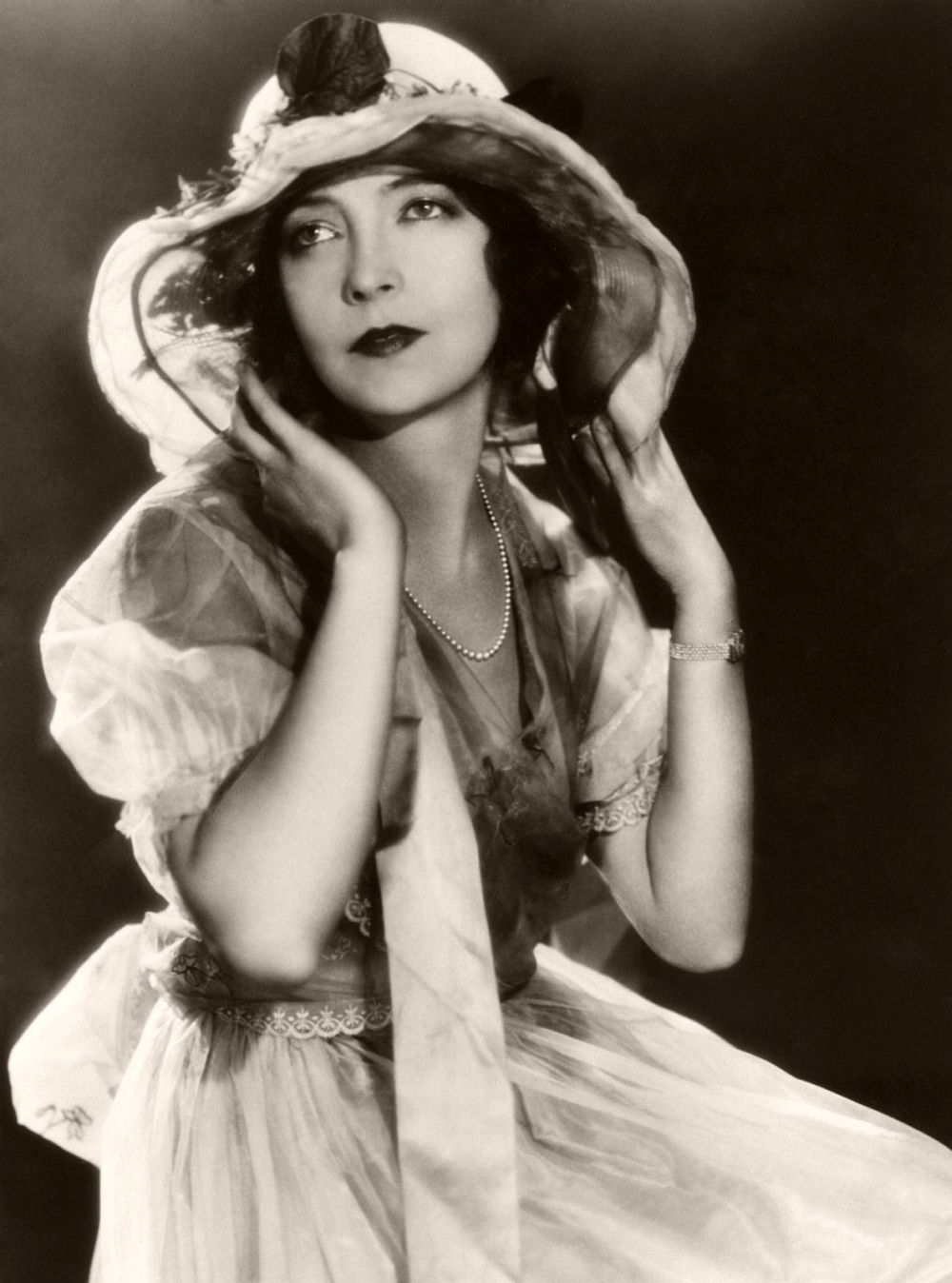

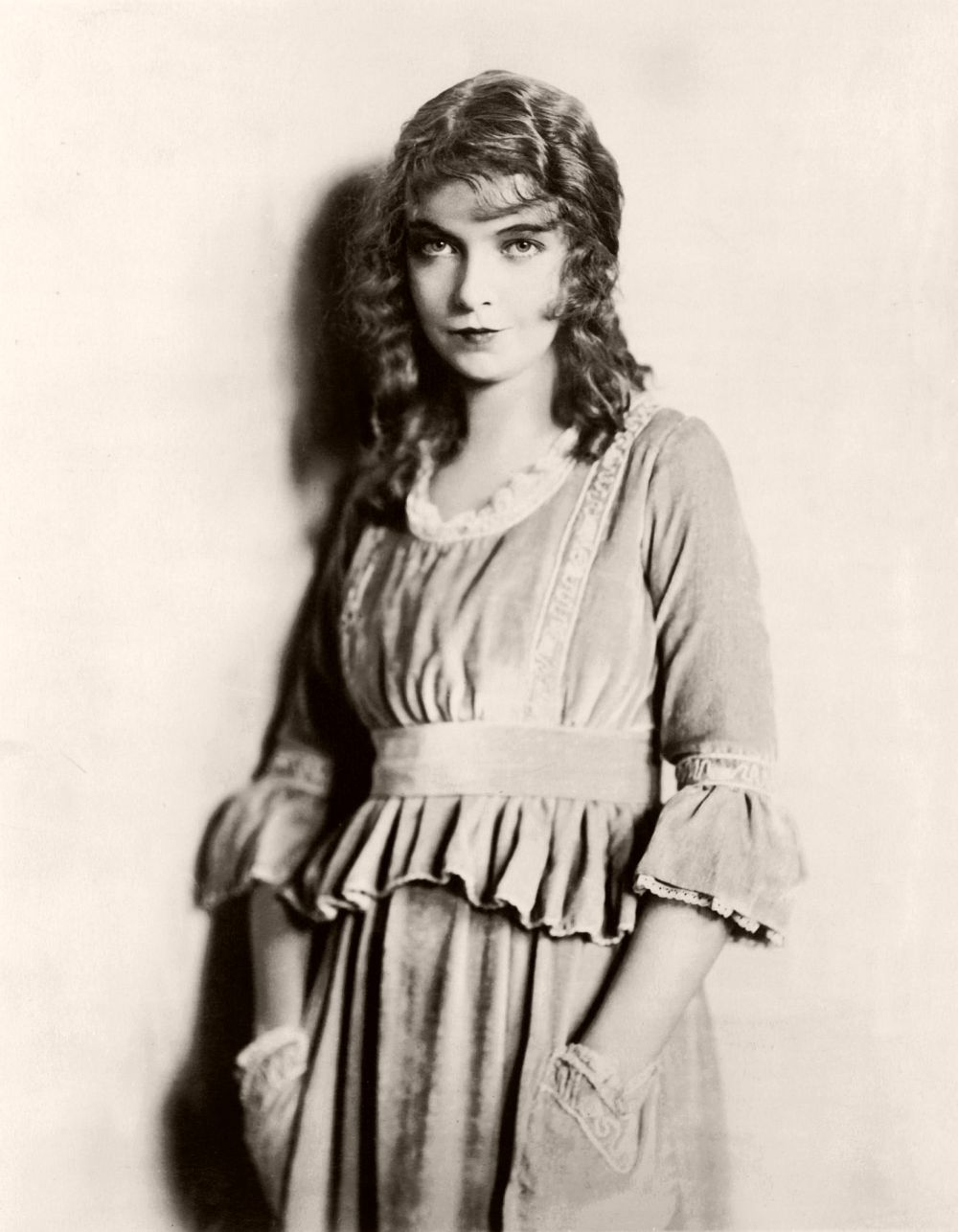
circa 1924: Lillian Diana Gish, originally Lillian de Guiche (1893 – 1993). She played a lot of waif type heroines during her silent film career but never quite made the successful transition to talking pictures.