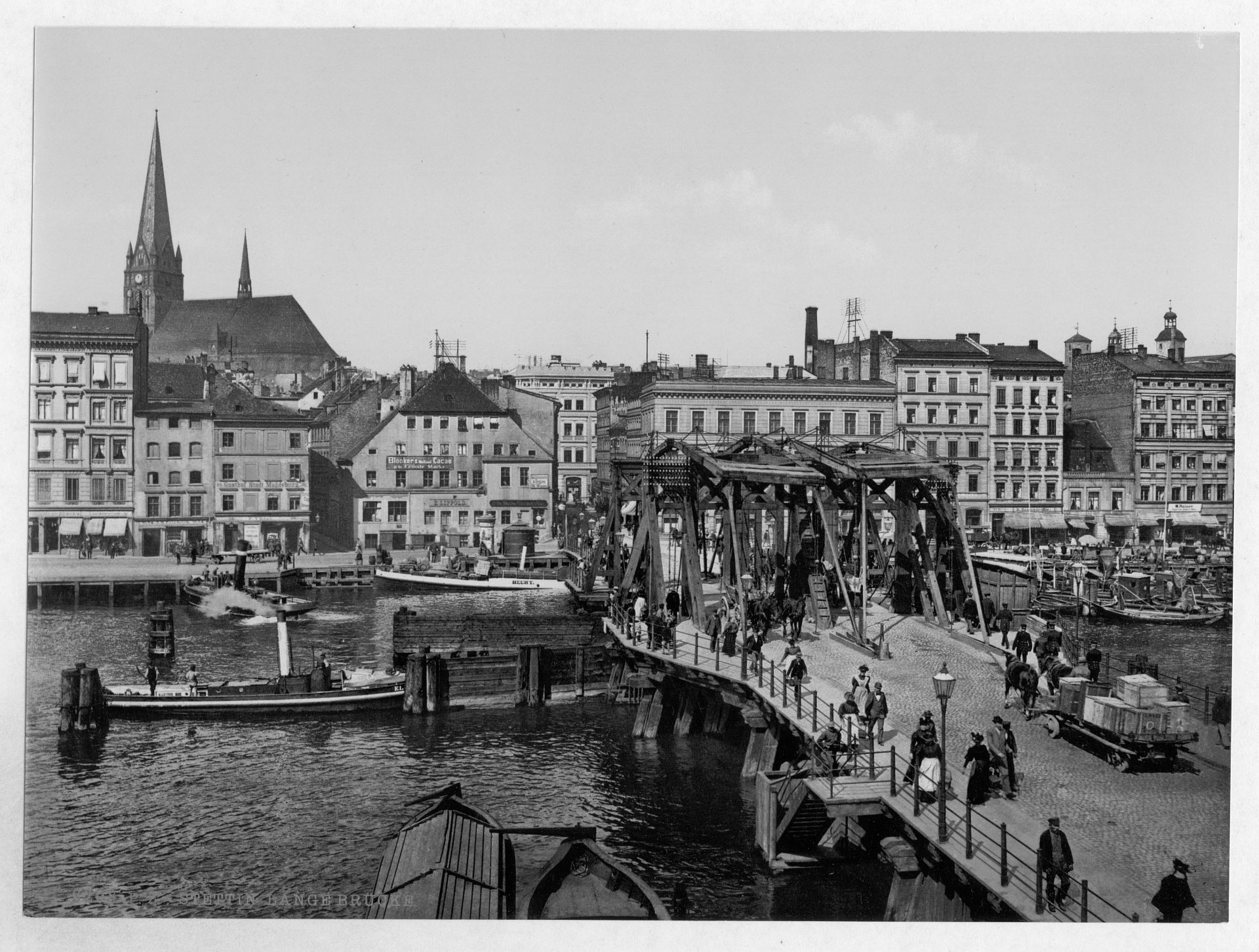
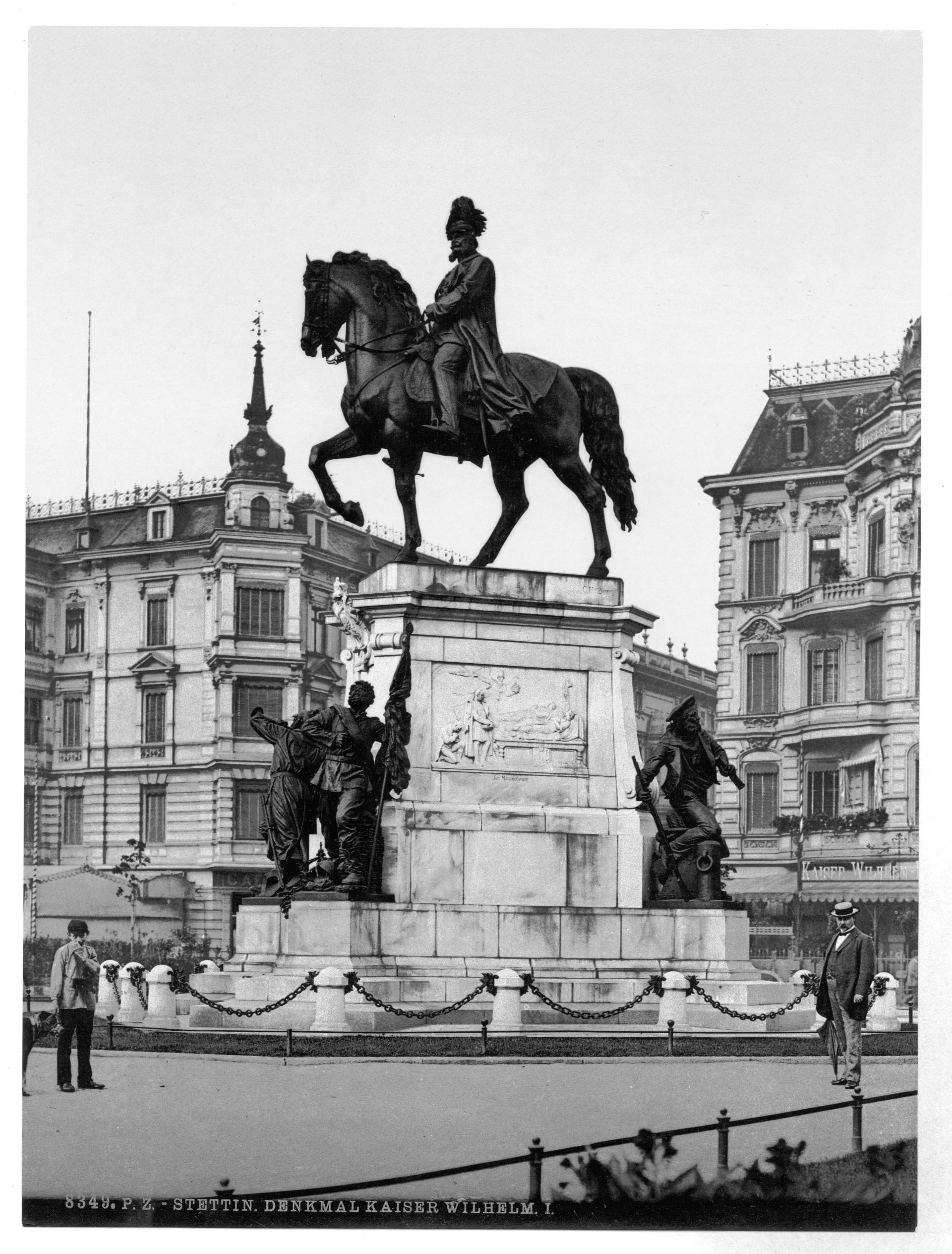
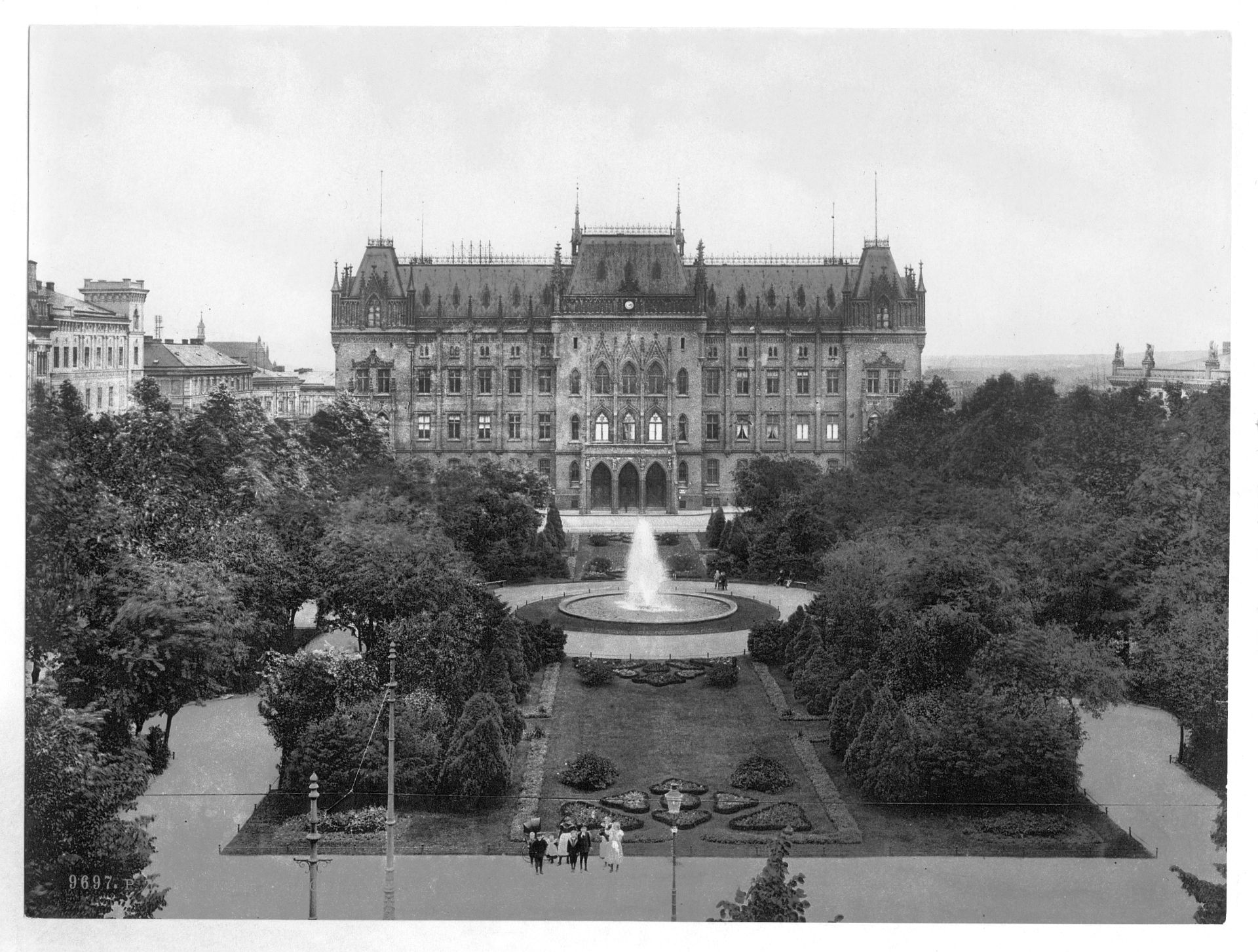
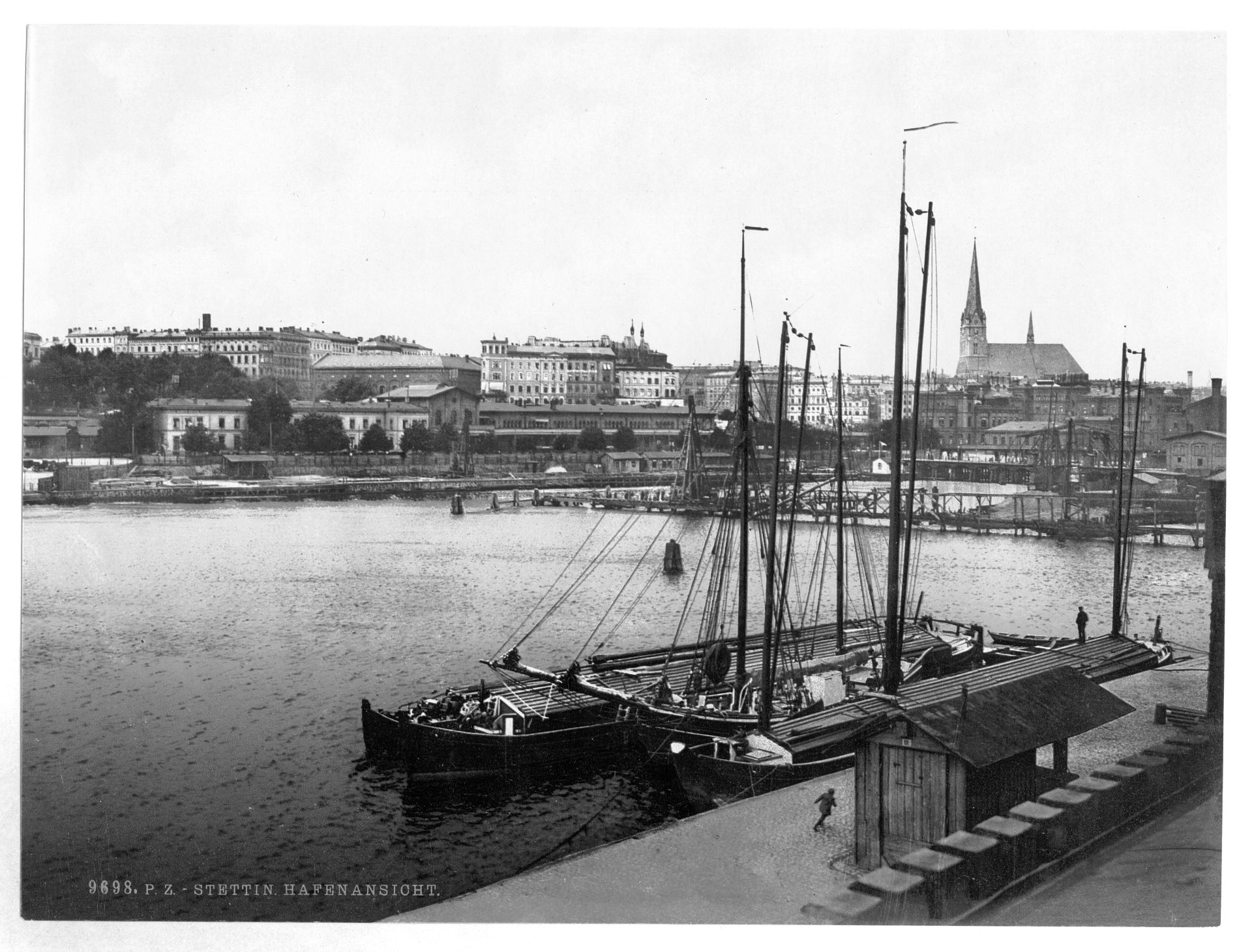
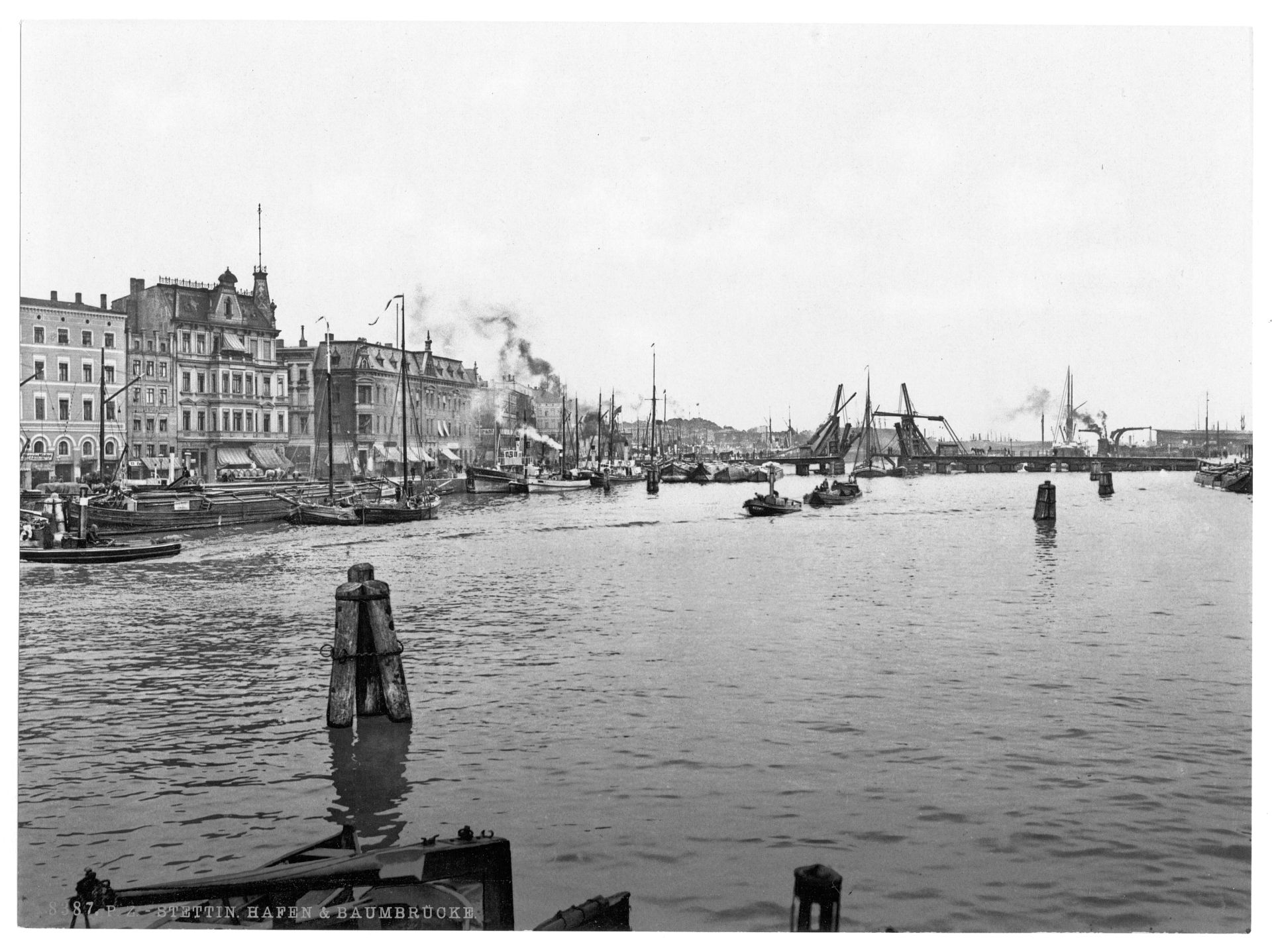
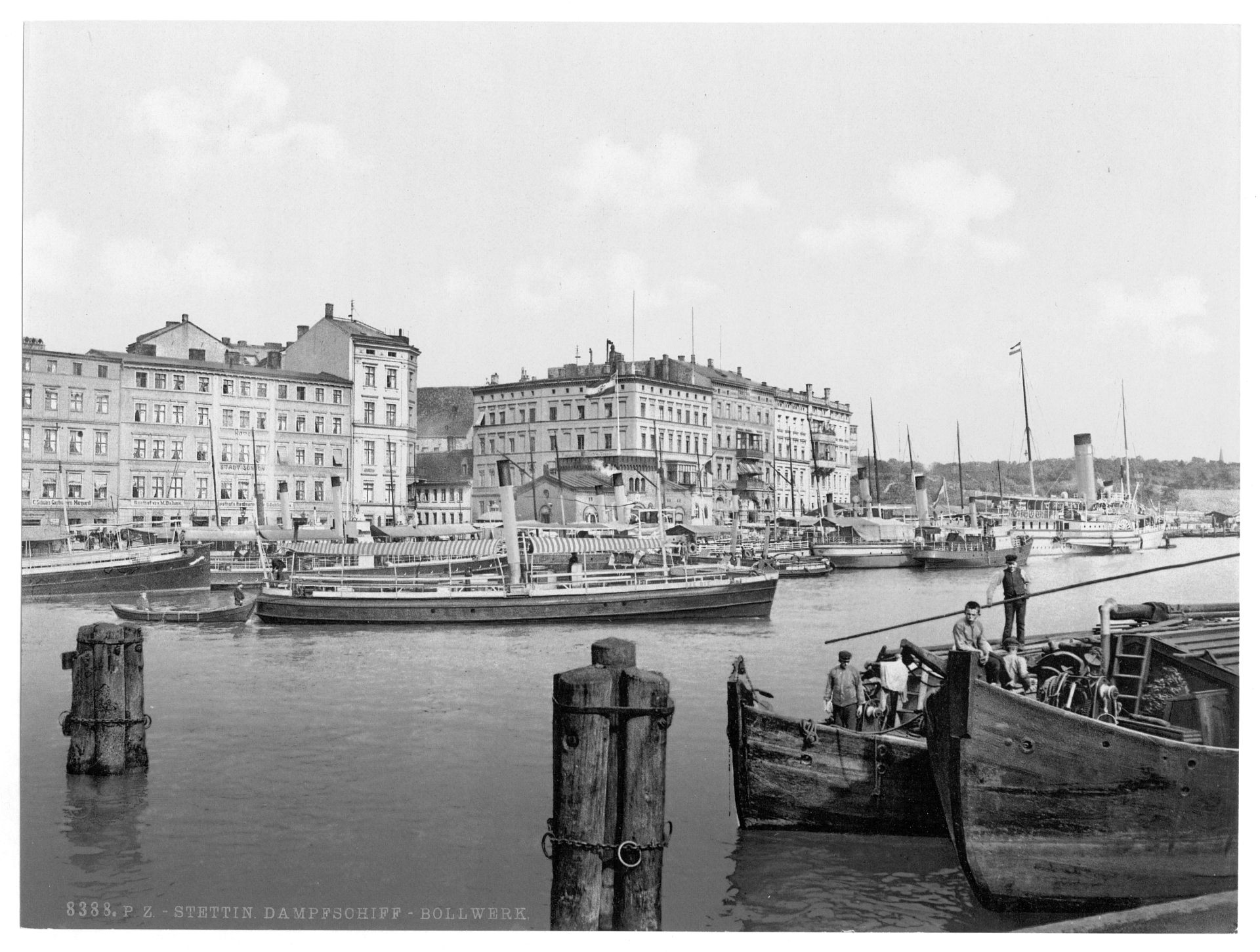
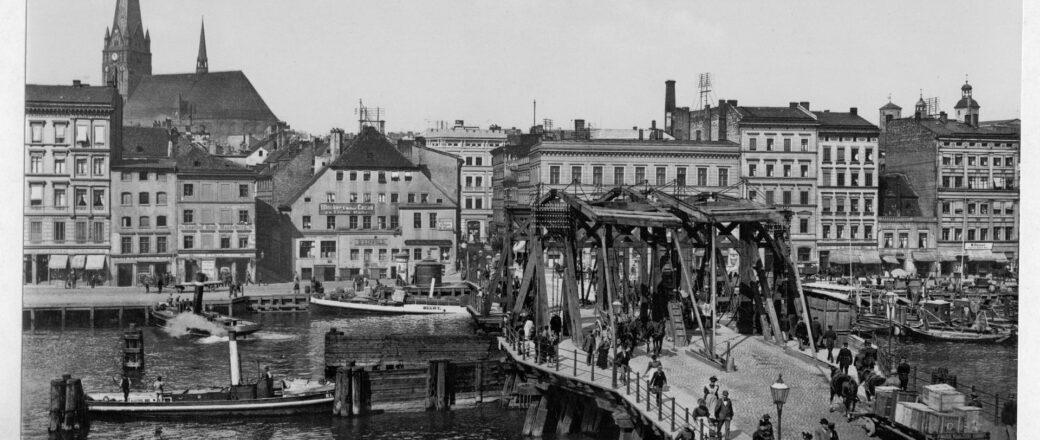Stettin developed into a major Prussian port and became part of the German Empire in 1871. While most of the province retained its agrarian character, Stettin was industrialised, and its population rose from 27,000 in 1813 to 210,000 in 1900 and 255,500 in 1925. Major industries that flourished in Stettin from 1840 were shipbuilding, chemical and food industries, and machinery construction. Starting in 1843, Stettin became connected to the major German and Pomeranian cities by railways, and the water connection to the Bay of Pomerania was enhanced by the construction of the Kaiserfahrt (now Piast) canal. The city was also a scientific centre; for example, it was home to the Entomological Society of Stettin.
On 20 October 1890, some of the city’s Poles created the “Society of Polish-Catholic Workers” in the city, one of the first Polish organisations. In 1897, the city’s ship works began the construction of the pre-dreadnought battleship Kaiser Wilhelm der Grosse. In 1914, before World War I, the Polish community in the city numbered over 3,000 people, contributing about 2% of the population. These were primarily industrial workers and their families who came from the Poznań (Posen) area and a few local wealthy industrialists and merchants. Among them was Kazimierz Pruszak, director of the Gollnow industrial works and a Polish patriot, who predicted the eventual “return” of Szczecin to Poland.