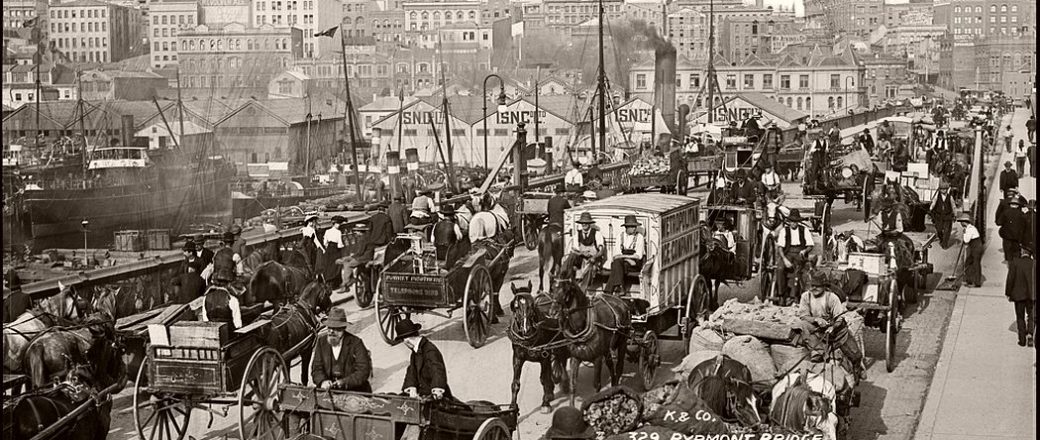
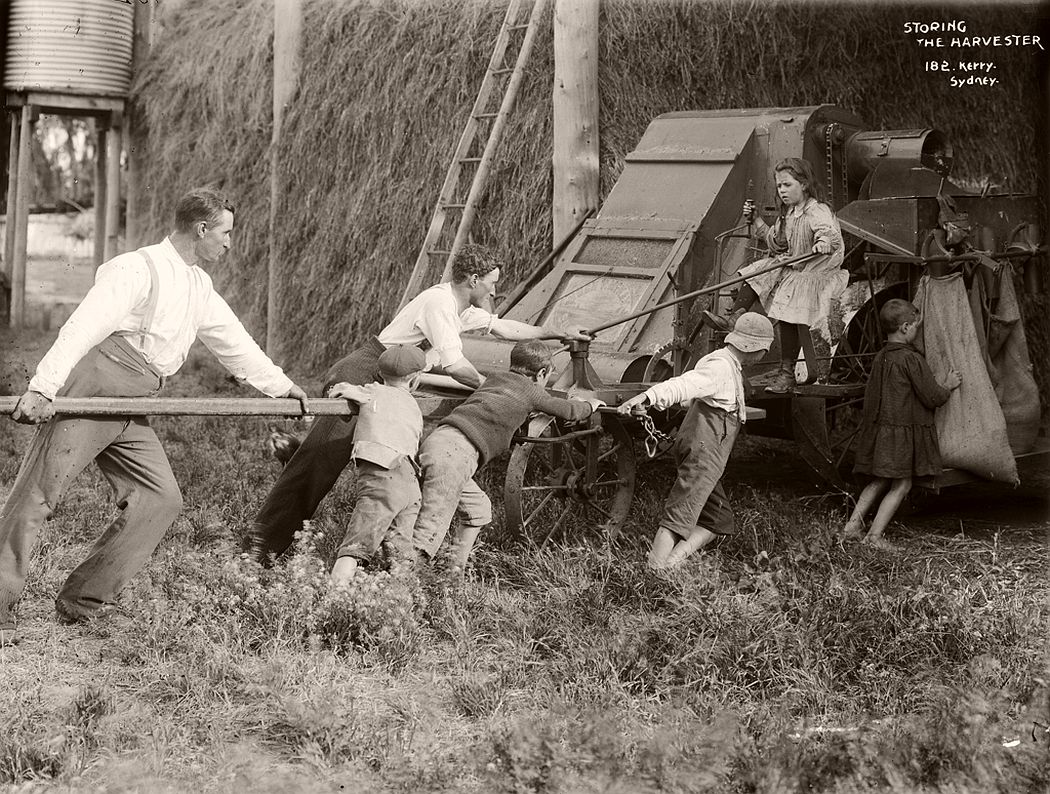
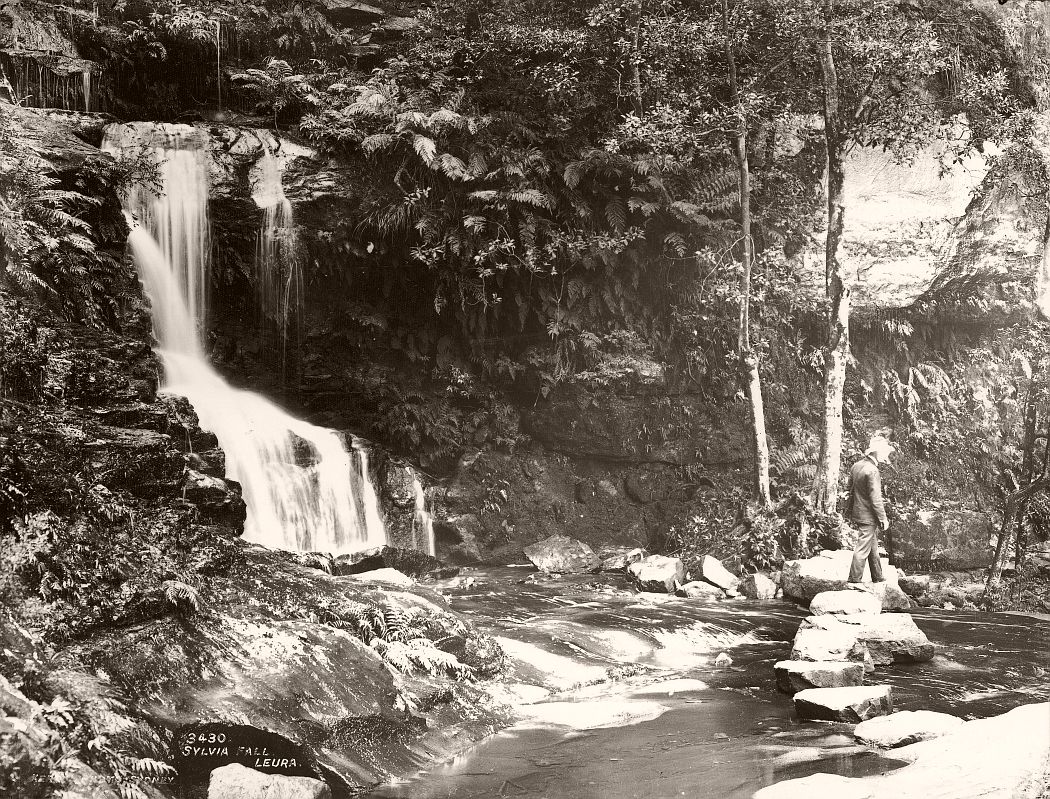
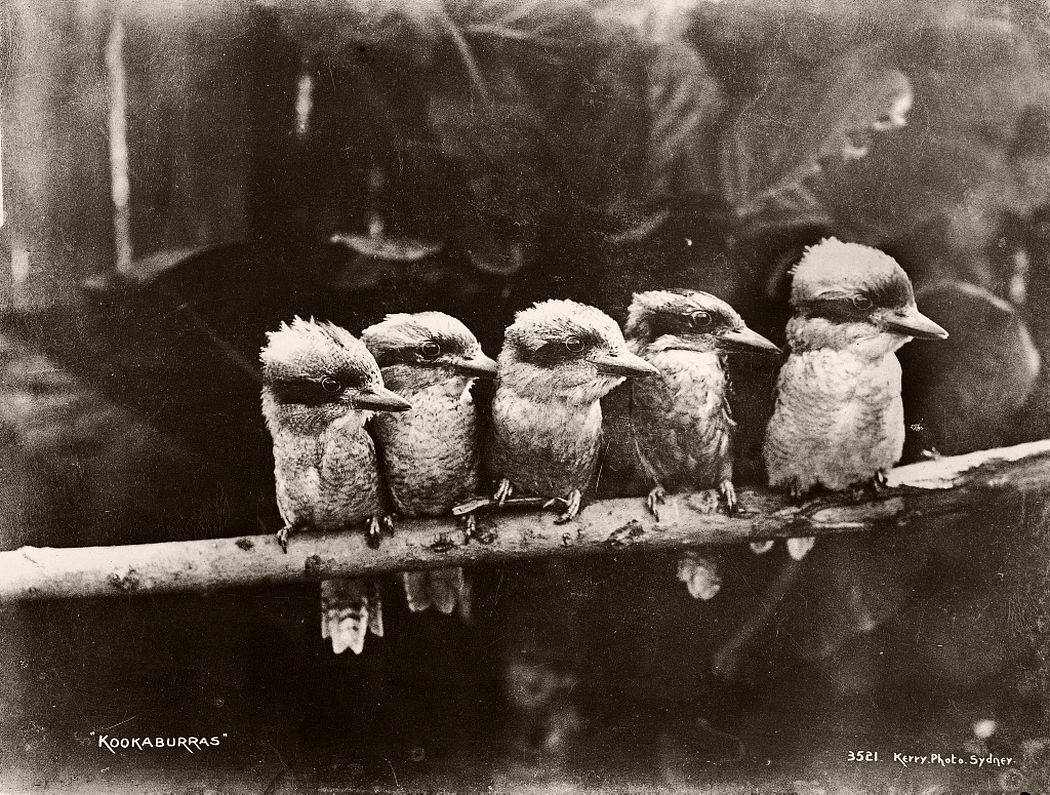
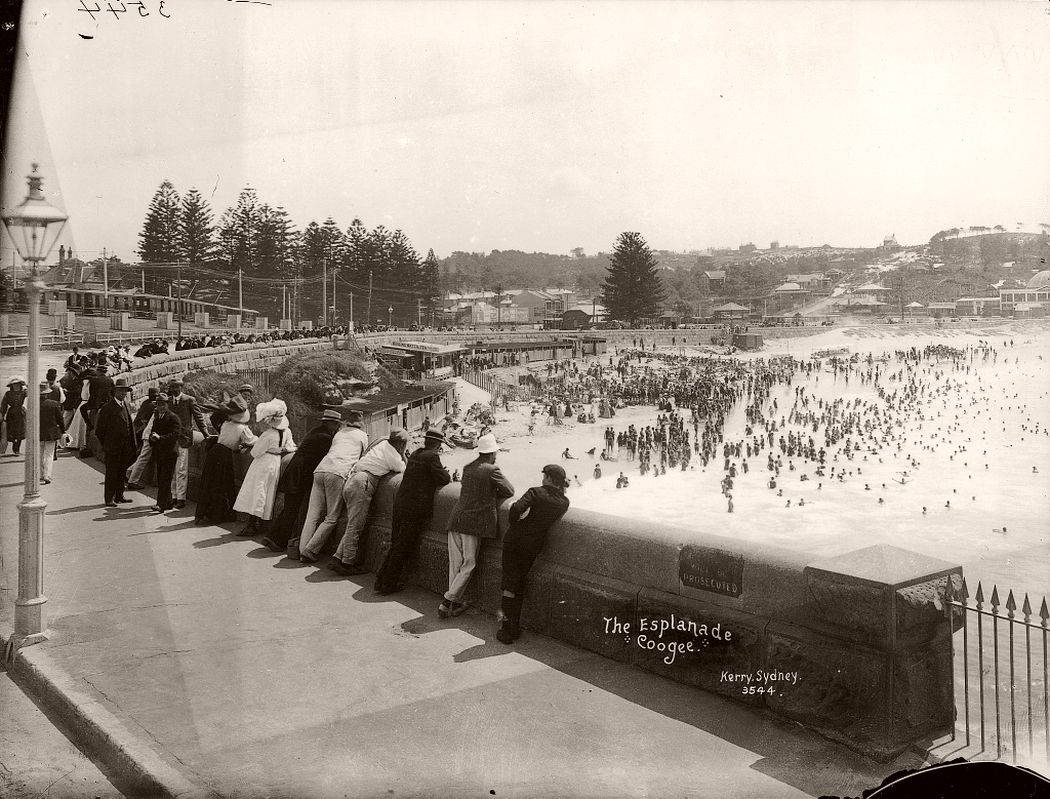
Charles Kerry (1857 – 1928) began working in the Sydney photo studio of A.H. Lamartiniere in 1875. When Lamartiniere fled from creditors a few years later, Kerry took charge of the company, paying debts and turning around the business. Initially Kerry specialised in portraits but branched into photographing Sydney scenery and society. He was also active in the postcard business. Eventually Kerry turned this small studio into Australia’s largest photographic establishment.
In 1885 Kerry was asked to prepare an exhibit of Aboriginal portraits and corroboree pictures for the 1886 Colonial and Indian Exhibition. In 1890, the Governor of New South Wales, Lord Carrington, appointed Kerry as his official photographer.
In 1891 Kerry was commissioned to photograph the Jenolan and Yarrangobilly Caves. An innovative artist, Kerry used the still-experimental technique of magnesium flash powder to capture the interior of the Jenolan Caves. By 1900 Kerry handled the major illustrations for the local press. In 1908 he photographed the visit of the American Fleet and the Burns–Johnson heavyweight boxing match. To gain an aerial view of the arrival of the Great White Fleet he mounted a camera on a box kite.
In 1895, Kerry began a Squatter’s Service, travelling around the colony photographing squatter’s land, homesteads, families and livestock.
Charles Kerry first visited Kiandra in 1894 to pursue his mining interests, he returned in 1896 on a photographic tour. The following year with practically no skiing experience was assisted by group including Kiandra ski club members on an historic photography tour to the summit of Mount Kosciuszko. In 1909 he was elected Founding President of the Kosciusko Alpine Club, which led to the opening up of the area for skiing and the naming of a run after him.
By 1898 he had the largest photographic establishment in Australia, a three floor building at 310 George Street, Sydney.
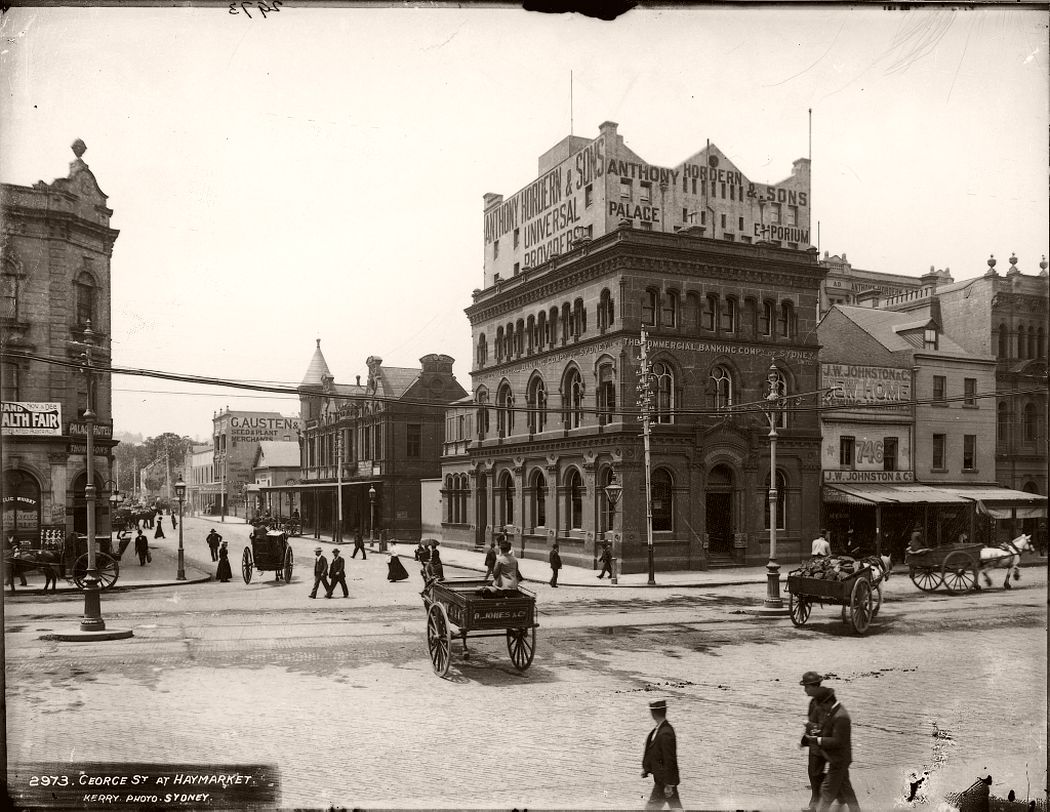

George Street at Haymarket looking East into Hay Street, note the building with the number 746 George Street to confirm location of this photo. 744 is currently a Library.’, Kerry and Co, Sydney, Australia, c. 1884-1917

Several skiers from the 1900 Kiandra Snow Shoe Carnival posing in front of a building in the snow. Photo: Charles Kerry
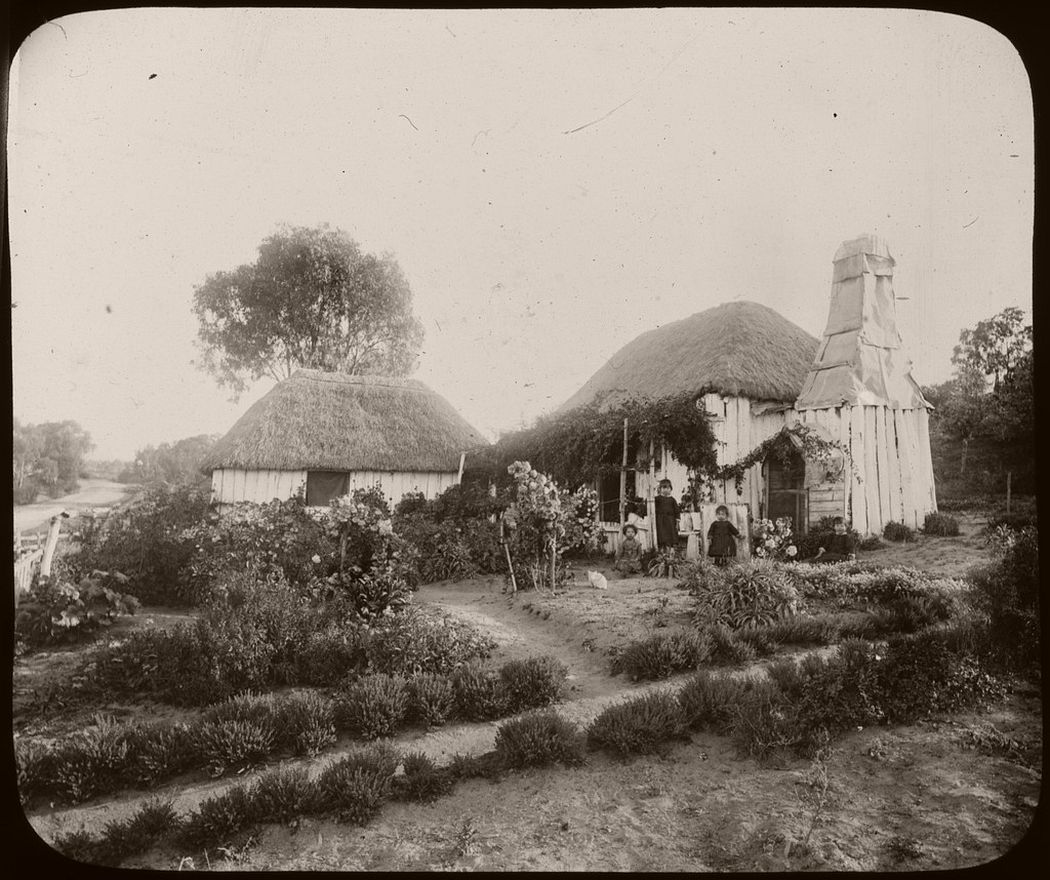
Three children and a white cat in the garden of a thatched house, Australia, ca. 1886. Photo: Charles Kerry













